Definition: Acute Inflammation
Localized, short-term immune response triggered by tissue injury or infection. (Not a synonym for infection)
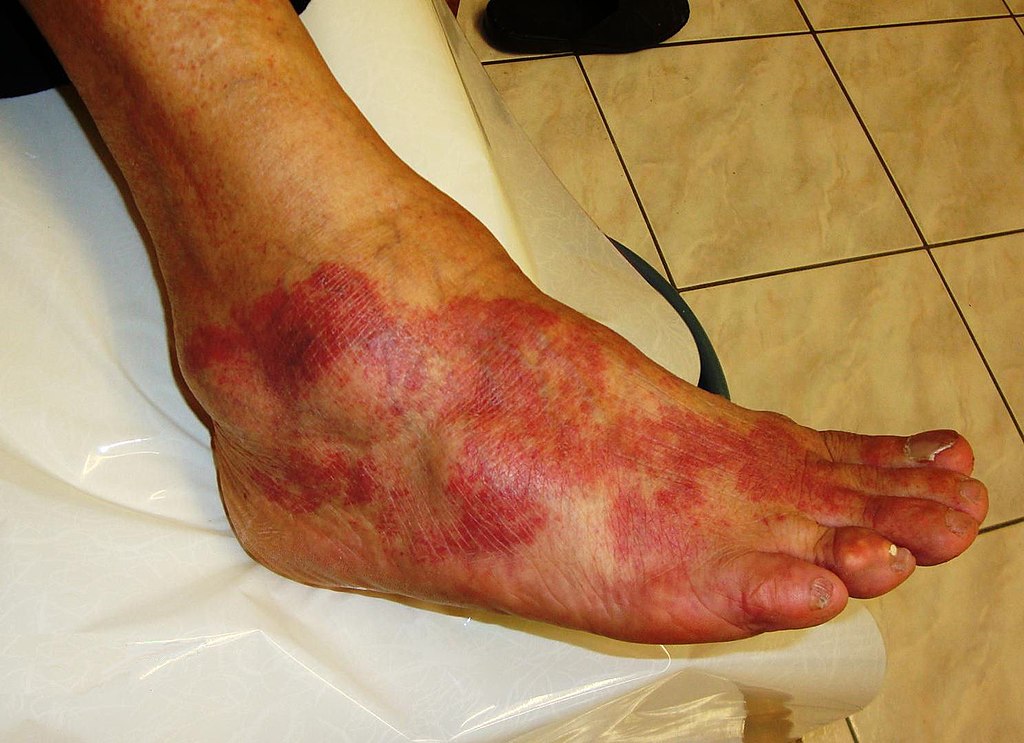
Cardinal Signs of Acute Inflammation
| Cardinal Sign | Description | Mediators |
|---|---|---|
| Rubor (Redness) | Vasoactive mediators → arteriolar smooth muscle relaxation → ↑ blood flow | Prostaglandins, bradykinin, histamine, NO |
| Dolor (Pain) | Due to stimulation of free nerve ending | Bradykinin, PGE2 |
| Calor (Heat) | Vasodilation → Increased blood flow → Warmth | Prostaglandins, bradykinin, histamine, NO |
| Tumor (Swelling) | Damage to endothelium → separation of endothelial junction → ↑ vascular permeability → leakage of exudate from postcapillary venule | Histamine, Leukotrienes, Serotonin |
| Functio Laesa | Loss of function or impaired function in the affected area | – |
Sequential vascular events in Acute Inflammation
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Vasoconstriction of arterioles | Brief vasoconstriction due to neurogenic reflex |
| 2. Vasodilation of arterioles | Histamine and other vasodilators relax vascular smooth muscle, leading to increased blood flow |
| 3. Increased permeability of venules | Histamine and other mediators cause endothelial cell contraction, resulting in endothelial gaps and increased vascular permeability |
| 4. Swelling of tissue (tumor, edema) | Transudate (fluid low in proteins and cells) moves into interstitial tissue due to increased hydrostatic pressure |
| 5. Reduced blood flow | Outflow of fluid into interstitial tissue exceeds lymphatic drainage capacity, leading to reduced blood flow |
- Fluid exudation
- endothelial injury
- ↑ post-capillary venule permeability
- vasodilation
- Leukocyte activation
- emigration
- chemotaxis (bacterial products, complement, chemokines)
- phagocytosis
- killing
- Potential outcomes
- collagen deposition resulting in altered structure and function
Acute Inflammation vs. Chronic Inflammation
| Acute Inflammation | Chronic Inflammation | |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenesis | Microbial pathogens, trauma, burns | Persistent AI, foreign bodies, autoimmune disease, certain types of infection (eg TB, Leprosy) |
| Primary Cells Involved | Neutrophils | Monocytes/macrophages (Key cells), B and T lymphocytes, plasma cells, fibroblasts |
| Primary Mediators | Histamine (Key mediator), prostaglandins, leukotrienes | Cytokines (e.g., IL-1), growth factors |
| Necrosis | Present | Less prominent |
| Scar Tissue | Absent | Present |
| Onset | Immediate | Delayed |
| Duration | Few days | Weeks, months, years |
| Outcome | Complete resolution, progression to chronic inflammation, abscess formation | Scar tissue formation, disability, amyloidosis |
| Main Immunoglobulin | IgM | IgG |
| SPE Effect | Mild hypoalbuminemia | Polyclonal gammopathy; greater degree of hypoalbuminemia |
| Peripheral Blood | Neutrophilic leukocytosis | Monocytosis |
Preparing for USMLE Step 1? Check out our Mastery Course here


