Snapshot
- An 28-year-old woman presents with colicky abdominal pain. She fidgets around and sporadically has weeping spells, reports tingling in her fingers and toes, and has no significant past medical history with no official psychiatric history. On physical exam, she is found to be tachycardic. Her abdominal exam is normal, without tenderness on palpation. Neurologic exam is normal. Abdominal radiographs are completely normal. Porphobilinogen was found to be positive in high titers in her urine.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
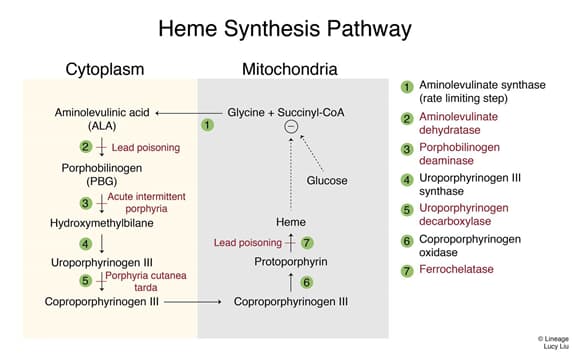
- acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is an inherited metabolic disease resulting from deficiency in the heme synthesis pathway enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase (PBD)
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- AIP is the most common type of acute porphyria
- still relatively rare
- AIP is the most common type of acute porphyria
- demographics
- women > men
- 20-40 years of age
- risk factors
- female gender
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- pathobiology
- attacks are precipitated by an exposure
- exposure increases demand of the heme pathway
- this results in accumulation of intermediates aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG)
- both are neurotoxic
- this results in accumulation of intermediates aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and porphobilinogen (PBG)
- precipitating factors
- most common drugs
- cytochrome P-450 inducers
- anticonvulsants
- oral contraceptive pills
- smoking
- infection
- starvation
- fluctuating hormones (menstrual cycle in women)
- most common drugs
- exposure increases demand of the heme pathway
- attacks are precipitated by an exposure
- pathobiology
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal dominant
- mutations
- HMBS (also known as PBGD), encoding PBD
- inheritance pattern
- Prognosis
- most patients fully recover
- < 5% have recurrence
Presentation
- Symptoms
- often nonspecific and vague
- Physical exam
- vitals
- tachycardia
- hypertension
- vitals
- the rest of physical exam is often normal
Imaging
- Radiographs
- abdominal radiography
- indications
- often initially obtained due to nonspecific nature of symptoms
- findings
- indications
- abdominal radiography
- normal
Studies
- Labs
- serum studies
- may see hyponatremia
- urine studies
- serum studies
- ↑ PBG, aminolevulinic acid
Differential
- Small bowel obstruction
- tenderness on palpation
- Lead poisoning
- no elevated PBG in urine
Treatment
- Remove precipitating factors
- Medical
- heme and glucose
- indications
- for symptomatic attacks
- indications
- heme and glucose
- to prevent permanent neurologic damage
Complications
- Chronic neuropathic pain
- treatment
- gabapentin
- treatment


