Snapshot
- A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency room with a 1-day history of fever and a new skin rash. He is taking methicillin for a soft tissue infection. On physical exam, he has costovetebral tenderness, and a diffuse maculopapular rash over his trunk. His serum creatinine is elevated at 3 mg/dL. Urinalysis reveals white blood cells. Further testing with Wright stain is positive for eosinophils in the urine.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- acute interstitial nephritis (AIN), also known as tubulointerstitial nephritis, is an acute immune-mediated interstitial inflammation of the kidneys
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- middle-aged adults
- demographics
- Etiology
- drug-induced hypersensitivity (majority of cases)
- typically developed between 1 week to 9 months
- 5 Ps
- Pee (diuretics, especially sulfa ones)
- Pain-free (NSAIDs)
- Penicillins and cephalosporins
- Proton pump inhibitors
- rifamPin
- systemic infections
- autoimmune diseases
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- sarcoidosis
- drug-induced hypersensitivity (majority of cases)
- Pathogenesis
- type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- T-cell-mediated attack on tubular cells
- Prognosis
- typically resolves after withdrawal of inciting agent
Presentation
- Symptoms
- primary symptoms
- fever
- hematuria
- arthralgia
- can be asymptomatic
- primary symptoms
- Physical exam
- rash
- maculopapular
- rash
- flank/costovertebral angle tenderness
Studies
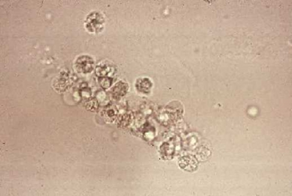
- Labs
- serum eosinophilia
- elevated serum creatinine
- Urinalysis with microscopy and sediment analysis
- hematuria
- eosinophiluria
- seen with Hansel or Wright stain
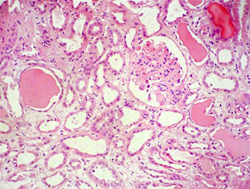
- Renal biopsy
- not usually indicated
- Histology
- severe tubular damage
- interstitial edema
- T-cell and eosinophilic infiltration
- Diagnostic criteria
- elevated creatinine
- urinalysis with white cell casts and eosinophiluria
Differential
- Acute tubular necrosis from NSAIDs
- no rash or eosinophils
- Renal atheroemboli
- also presents with eosinophiluria, eosinophilia, and skin rash
- rash is typically livedo reticularis with digital infarcts and not maculopapular
Treatment
- Conservative
- Medical
- glucocorticoids
- indications
- glucocorticoids
- if creatinine continues to rise after stopping drugs
Complications
- Renal failure requiring dialysis


