Snapshot
- A 11-year-old girl with Down syndrome presents with a few weeks of low-grade fever. She is otherwise feeling well, with no signs of infection. Blood-work shows elevated WBCs, low neutrophil count, and anemia. Blood cultures are drawn and come back positive for Pseudomonas.
Introduction
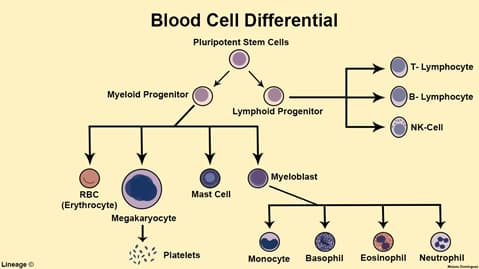
- Acute leukemia of lymphoid precursor cells that occurs in children
- Crowding of bone marrow leads to bone marrow failure
- Subtypes
- Epidemiology
- < 15 years
- most common type of cancer and leukemia in children
- Associated conditions
- leukemia in Down syndrome children < 5 years = AML
Presentation
- Symptoms
- most common symptom is fever
- acute onset
- recurrent infections
- bleeding
- fatigue
- Physical exam
- mediastinal mass from infiltration of thymus
- hepatosplenomegaly
- lymphadenopathy
Evaluation
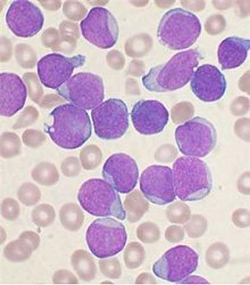
- Peripheral blood smear
- ↑ lymphoblasts (high nuclei to cytoplasm ratio)
- CBC reflects bone marrow failure
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- ↓ mature WBCs
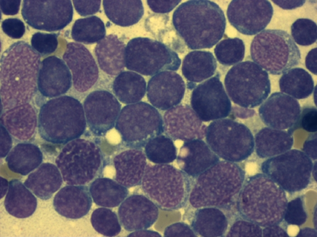
- Bone marrow aspiration with cytogenetics
- ↑ lymphoblasts
- TdT+, a marker of pre-T and pre-B cells
- T-cell ALL
- CD2+
- CD3+
- B-cell AML
- CD10+
- CD19+
- negative MPO (myeloperoxidase)
- t(12:21)
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Prophylaxis to CNS (standard chemotherapy does not penetrate blood-brain barrier)
- intrathecal chemotherapy
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- very responsive to therapy
- Complications
- likes to spread to CNS and testes


