Snapshot
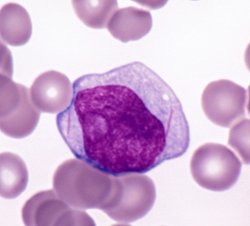
- A 60-year-old man presents with fever, long-standing fatigue, and shortness of breath on exertion. He also complains of easy bruising and occasional bleeding from his gums. On physical exam, he has cervical lymphadenopathy and marked hepatosplenomegaly. Peripheral blood smear shows large blasts.
Introduction
- Acute leukemia with pancytopenia
- Epidemiology
- median onset 65 years of age
- Subtypes
- M3 aka acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML)
- associated with DIC
- presence of Auer rods
- peroxidase positive eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions
- M3 aka acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML)
- Risk factors
- alkylating chemotherapy
- radiation
- myeloproliferative disorders
- Down syndrome
Presentation
- Symptoms of pancytopenia (high WBC count but WBCs are dysfunctional)
- fatigue
- dyspnea
- infection due to dysfunctional blasts
- bleeding
- Physical exam
- lymphadenopathy
- fever
- hepatosplenomegaly
Evaluation
- Peripheral blood smear
- > 20% blasts in blood smear
- Most accurate test = flow cytometry
- Bone marrow biopsy with cytogenetics
- myeloperoxidase (MPO) positive
- CBC
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- ↓ mature WBCs
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- Initial treatment with chemotherapy
- to induce remission
- cytarabine
- Bone marrow transplant after remission
- especially for cytogenetics revealing high chance of relapse
- All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) to those with M3 (APL)
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- prognostic indicator is cytogenetics
- 90% complete response rate from initial chemotherapy in those with good cytogenetics
- relapse rate > 50% with median survival 3-12 months
- Complications
- febrile neutropenia
- DIC
- gout
- tumor lysis syndrome


