Overview
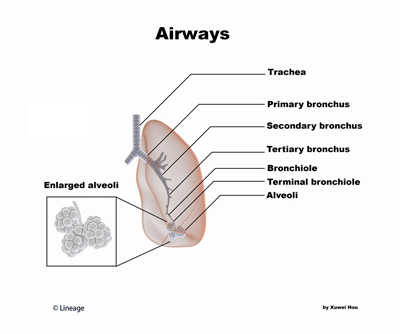
- Conducting Airways
- “conducting zone” includes:
- nose
- nasopharynx
- larynx
- trachea
- contains a cartilaginous layer composed of C-shaped hyaline cartilages
- prevent collapse of tracheal lumen, especially during expiration
- contains a cartilaginous layer composed of C-shaped hyaline cartilages
- bronchi
- contain a cartilaginous layer composed of discontinuous cartilage plates
- bronchioles
- terminal bronchioles
- bring air into and out of lungs
- warm, humidify, and filter air
- anatomic dead space
- do not participate in gas exchange
- walls contain smooth muscle
- sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation regulates airway diameter
- mechanism for altering airway resistance and airflow
- sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation regulates airway diameter
- “conducting zone” includes:
- Respiratory Airways
- “respiratory zone” includes:
- alveolar ducts
- participate in gas exchange
- structures are lined with alveoli
- exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveoli and pulmonary capillary blood occurs rapidly and efficiently across alveoli
- alveolar walls are thin and have large surface area for diffusion
- blood-gas barrier = alveolar type I cell – interstitium – capillary endothelial cell
- “respiratory zone” includes:


