Overview
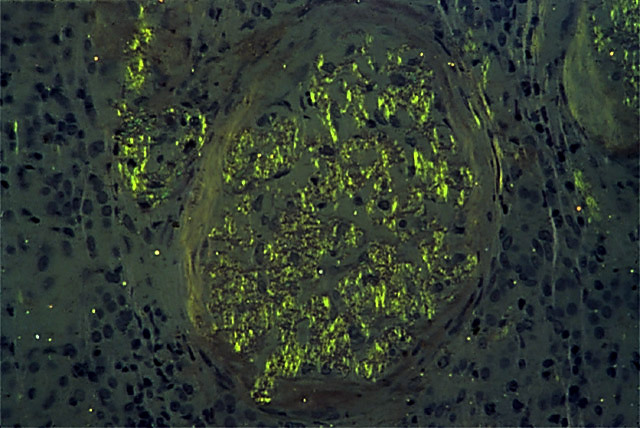
- Amyloid is misfolded protein that takes the form of a beta-pleated sheet
- the protein cannot be degraded by cellular enzymes
- results in accumulation in the extracellular space
- the deposited mass of the misfolded protein is damaging to tissues
- Diagnosis made by demonstrating
- apple-green birefringence of Congo red stain under polarized light
- Amyloid can form from a variety of proteins but the above characterisitic are shared properties
- Amyloid can be localized or systemic
Systemic Amyloidosis
- Affects the entire body and can be of primary or secondary cause
- Primary
- result of AL amyloid deposition
- derived from Ig light chain
- classically seen in multiple myeloma
- result of AL amyloid deposition
- Secondary
- Clinical findings
- deposition in glomerulus
- results in nephrotic syndrome
- deposition in the heart
- results in arrhythmias and/or restrictive cardiomyopathy
- deposition in glomerulus
- deposition in liver, spleen, tongue, intestine
Localized Amyloidosis
- Affects only a specific organ


