Snapshot
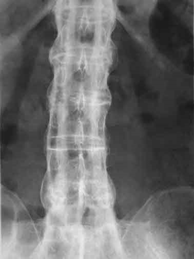
- A 21-year-old man presents to his physician’s clinic with lower back pain. He reports the pain is accompanied by stiffness, is worse in the morning, and improves with exercise. He denies any radiation of pain or bowel and bladder incontinence. On physical exam, there is decreased anterior flexion of the lumbar spine. Laboratory testing is positive for HLA-B27. A plain radiograph of the spine is shown.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the sacroiliac joint and spine
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- more common in men
- peak onset age is 15-35 years of age
- demographics
- Etiology
- unknown but may involve both genetic (e.g., HLA B-27 positivity) and environmental factors
- Pathogenesis
- unclear but involves inflammation, bone erosion, and spur formation
- can result in spinal fusion and costovertebral and costosternal
ankylosis
- can result in spinal fusion and costovertebral and costosternal
- involves the entheses
- connective tissue between bone and a tendon or ligament
- unclear but involves inflammation, bone erosion, and spur formation
- Associated conditions
- psoriasis
- inflammatory bowel disease
- aortic regurgitation
- Prognosis
- may lead to chronic pain and stiffness
Presentation
- Symptoms
- back pain
- worse in the morning and lasts approximately 30 minutes
- pain improves with activity
- stiffness of the spine
- anterior uveitis
- photophobia
- watering and redness of the eye
- back pain
- Physical exam
- may have stooped posture
- positive Schober test
- demonstrates limited spine flexibility
- decreased chest wall expansion
Imaging
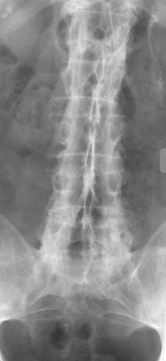
- Radiography
- indication
- gold standard for evaluating and supporting the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
- findings
- indication
- “bamboo spine”
Studies
- Labs
- HLA-B27 positivity
- seen in > 90% of patients
Differential
- Mechanical low back pain
- Enteropathic arthritis
- Reactive arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
Treatment
- Conservative
- patient education and exercise
- indication
- mainstay of treatment
- indication
- patient education and exercise
- Medical
- nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- indication
- considered first-line treatment for managing pain and stiffness
- indication
- tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors
- indication
- typically used in patients who do not respond to conservative and NSAID treatment
- medications
- adalimumab
- indication
- nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- etanercept
Complications
- Low bone density
- Spine fracture leading to injury of the spinal cord
- Restrictive lung disease


