Overview
- All are S-phase specific
Methotrexate
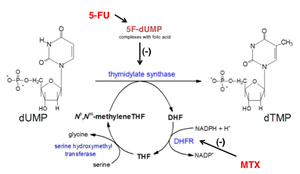
- Mechanism
- inhibits folate metabolism
- folic acid analog
- inhibits dihydrofolate reductase
- ↓ dTMP → ↓ DNA and ↓ protein synthesis
- inhibits folate metabolism
- Clinical use
- cancer
- leukemias
- lymphomas (except Hodgkin lymphoma)
- breast cancer
- choriocarcinoma
- sarcomas
- non-cancer
- rheumatoid arthritis
- psoriasis
- abortion
- ectopic pregnancy
- cancer
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- fatty change in liver
- macrovesicular
- teratogenic
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
- Mechanism
- pyrimidine analog
- bioactivated to 5F-dUMP
- covalently complexes to folic acid
- bioactivated to 5F-dUMP
- ↓ dTMP → ↓ DNA and ↓ protein synthesis
- synergistic with MTX
- pyrimidine analog
- Clinical use
- colon cancer
- basal cell carcinoma (topical)
- breast cancer
- ovarian cancer
- head and neck cancer
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- “rescue” with thymidine
- NOT reversible with leucovorin, in fact effects are stronger
- myelosuppression
- photosensitivity
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- Mechanism
- purine analog
- activated by HGPRTase
- ↓ de novo purine synthesis
- purine analog
- Clinical use
- leukemias
- ALL
- not CLL
- lymphomas
- not Hodgkin’s
- immunosuppression
- leukemias
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- GI
- liver
- 6-MP is metabolized by xanthine oxidase
6-Thioguanine (6-TG)
- Mechanism
- same as 6-MP
- Clinical use
- ALL
- can be given with allopurinol
- ALL
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- hepatotoxicity
Cytarabine (ara-C)
- Mechanism
- pyrimidine analog
- inhibits DNA polymerase
- pyrimidine analog
- Clinical use
- AML
- ALL
- lymphomas
- high-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Toxicity
- leukopenia
- thrombocytopenia
- megaloblastic anemia


