Aspirin (ASA)
- Mechanism
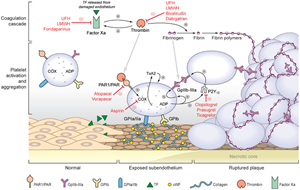
- acetylates and irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase in platelets
- both COX-1 (more important) and COX-2
- prevents conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A2 (normally secreted by active platelets)
- decreases platelet activation
- ↑ bleeding time
- PT and PTT unchanged
- acetylates and irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase in platelets
- Clinical use
- prevent MI
- prophylaxis against clotting in atrial arrhythmias and stroke
- analgesic
- antipyretic
- anti-inflammatory
- low dose reduces the incidence of colon cancer
- Toxicity
- GI bleeding
- hyperventilation
- tinnitus
- affects CN VIII
ADP receptor antagonists (thienopyridines)
- Drugs
- ticlopidine
- Mechanism
- blocks ADP-mediated platelet aggregation which decreases Gp IIb/IIIa expression via the P2y12 receptor
- prevents expression of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa by platelets
- inhibits binding of fibrinogen and clot formation
- Clinical use
- alternative to ASA
- reduce risk of thrombotic stroke
- post-stent surgery
- post-MI
- acute coronary syndrome
- unstable angina
- alternative to ASA
- Toxicity
- neutropenia (ticlopidine)
- thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (ticlopidine)
IIb/IIIa inhibitors
- Drugs
- abciximab
- eptifibatide
- tirofiban
- Mechanism
- Clinical use
- acute coronary syndromes
- percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
- Toxicity
- bleeding
- thrombocytopenia
PDE III inhibitors



