Snapshot
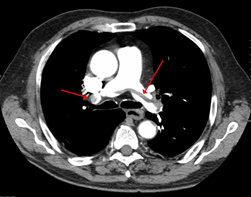
- A 23-year-old girl presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, and hemoptysis. She is found to be tachycardic; her pulse is 102/min. She has a history of DVTs requiring heparin at age 20. However, she has not been on any maintenance therapy. Clinical suspicion for a pulmonary embolism is high, and a chest spiral CT scan is ordered. The CT shows a saddle embolism. Heparin is started immediately.
Introduction
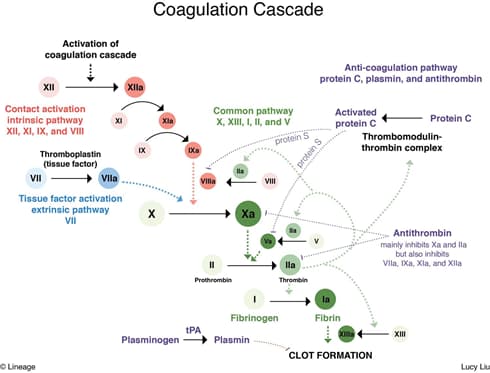
- Pathogenesis
- hypercoagulable state/thrombophilia due to deficiency in antithrombin III
-
- antithrombin III, an anticoagulant
- inhibits primarily thrombin (factor IIa) and factor Xa
- also inhibits activated factors VII, IX, XI, and XII
- remember, heparin enhances activity of antithrombin
- deficiency causes defect in anticoagulation pathway
- antithrombin III, an anticoagulant
- Genetics
- Risk factors
- liver disease (antithrombin III is synthesized in the liver)
- renal failure/nephrotic syndrome (loss of proteins in urine)
- heparin use (causes acquired reduction in antithrombin level)
Presentation
- Symptoms/physical exam
- may be asymptomatic
- thrombosis at a young age (venous > arterial)
- DVT
- PE
Evaluation
- Normal PT, PTT, and thrombin time
- Reduces the increase in PTT following heparin administration
- Heparin cofactor assay, an antithrombin functional assay
- ↓ antithrombin activity
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- For acute thrombosis
- heparin
- For maintenance therapy
- bridge to warfarin
- Medical therapy
- antithrombin replacement therapy
- peripartum and perioperative
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- at risk of thromboembolism
- lifetime risk 50-85%
- at risk of thromboembolism
- Prevention
- avoid pro-coagulant states
- OCPs
- hormone replacement therapy
- avoid pro-coagulant states
- Complications
- related to thromboembolism


