Dactinomycin (Actinomycin D)
- Mechanism
- intercalate between strands of DNA
- Clinical use
- Wilms’ tumor
- Ewing’s sarcoma
- rhabdomyosarcoma
- childhood tumors
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) and Daunorubicin
- Mechanism
- intercalate between strands of DNA
- noncovalent
- breaks DNA → decreased replication
- free radical generation
- inhibit topoisomerase
- intercalate between strands of DNA
- Clinical use
- Hodgkin’s lymphomas
- part of the ABVD combination regimen
- Adriamycin
- Bleomycin
- Vinblastine
- Dacarbazine
- part of the ABVD combination regimen
- solid tumors
- breast, endometrial, ovary, and lung
- myelomas
- sarcomas
- Hodgkin’s lymphomas
- Toxicity
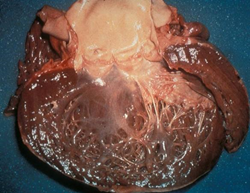
- cardiotoxicity
- dilated cardiomyopathy
- dexrazoxane used to prevent cardiotoxicity
- iron chelating agent
- prevents formation of free radicals
- does not “trap” free radicals
- myelosuppression
- alopecia
- cardiotoxicity
- tissue damage if extravasates into extravascular space
Bleomycin
- Mechanism
- free radical generation
- complexes with Fe and O2
- breaks DNA → decreased replication
- G2-phase specific
- free radical generation
- Clinical use
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- part of ABVD regimen for Hodgkin’s
- testicular cancer
- head and neck cancer
- skin cancer
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Toxicity
- pneumonitis
- skin changes
- myelosuppression is relatively insignificant
Etoposide (VP-16) and Teniposide
- Mechanism
- inhibits DNA topoisomerase II (think eTWOposide)
- breaks DNA → decreased replication
- late S- to G2-phase specific
- inhibits DNA topoisomerase II (think eTWOposide)
- Clinical use
- small cell carcinoma
- lung
- prostate
- testicular carcinoma
- small cell carcinoma
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- GI upset
- alopecia
Irinotecan and Topotecan
- Mechanism
- inhibits DNA topoisomerase I (think 1rinotecan)
- prevents DNA replication by inhibiting DNA unwinding
- inhibits DNA topoisomerase I (think 1rinotecan)
- Clinical use
- colon, ovarian, and small cell lung cancer
- Toxicity
- myelosuppression
- diarrhea


