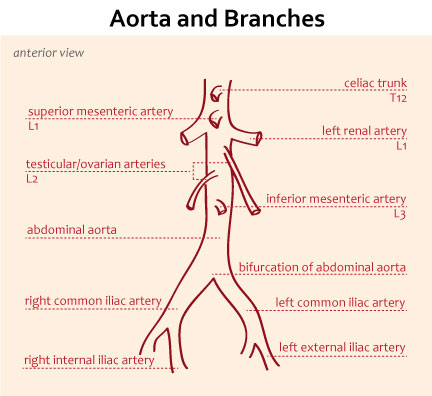
Overview
- Celiac trunk
- Superior mesenteric artery (SMA)
- branches
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- supplies distal portion of duodenum and head of pancreas
- middle colic artery
- supplies proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
- inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- branches
- Inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
- Renal arteries
- supplies kidneys and contribute to blood supply to adrenal glands
- Gonadal (testicular/ovarian) arteries
- testicular artery accompanies vas deferens into scrotum and supplies spermatic cord, epididymis, and testis
- ovarian artery enters the suspensory ligament of the ovary and supplies ovary
- anastomoses with the ovarian branch of uterine artery
- Common iliac arteries
- divides into the internal and external iliac arteries that supply pelvis
GI Blood Supply and Innervation
| Embryonic Gut Region | Artery | Parasympathetic Innervation | Vertebral Level | Structures Supplied |
| Foregut | Celiac Trunk | Vagus | T12 | Stomach to proximal duodenumLiver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen (mesoderm) |
| Midgut | SMA | Vagus | L1 | Distal duodenum to proximal 2/3 of transverse colon |
| Hindgut | IMA | Pelvic | L3 | Distal 1/3 of transverse colon to upper portion of rectumSplenic flexure is a watershed region |
Collateral Circulation
- Collateral circulation
- overview
- arterial anastomoses compensate for blockage of abdominal aorta
- external iliac artery and subclavian artery
- superior epigastric artery
- arises from the internal thoracic artery (internal mammary artery), a branch of the subclavian artery
- inferior epigastric artery
- arises from the external iliac artery
- superior epigastric artery and inferior epigastric artery anastomose, providing collateral circulation between the subclavian and external iliac arteries
- superior epigastric artery
- celiac trunk and SMA
- superior pancreaticoduodenal artery (celiac trunk) anastamoses with the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (SMA)
- SMA and IMA
- middle colic artery anastamoses with the left colic artery (IMA)
- IMA and internal iliac artery
- overview
- superior rectal artery (IMA) anastamoses with the middle rectal artery (internal iliac artery)
Watershed Areas
- Watershed areas and collateral circulation
- right colon
- marginal artery of Drummond supplies right colon though it is poorly developed in many patients
- splenic flexure
- marginal artery of Drummond is poorly developed in this area
- in hypotension and blood loss, this area can become ischemic
- rectosigmoid junction
- excellent collateral circulation above this point (left colic artery supplying marginal artery of Drummond) and below (superior and inferior rectal arteries supply the rectum) yet weak collateral circulation at this point
- collateral vessels to know in the colon (high yield)
- The marginal artery of Drummond
- anastomosis between the right, middle, and left colic arteries
- The arc of Riolan (meandering mesenteric artery)
- proximal anastomosis between the left and middle colic artery
- The marginal artery of Drummond
- right colon


