| Aphasia Syndromes |
| Aphasia | Lesion | Fluency | Comprehension | Repetition |
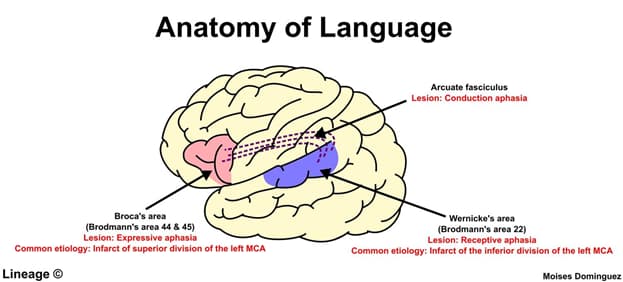
| Broca (expressive) | A lesion affectingBroca area (inferior frontal lobe) often secondary to an infarct involving thesuperior division of the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) | No | Yes | No |
| Wernicke (receptive) | A lesion affectingWernicke area (superior temporal lobe) often secondary to an infarct involving theinferior division of the left MCA | Yes | No | No |
| Conduction | A lesion affecting thearcuate fasciculus can be secondary to any lesion involving theperi-Sylvian area | Yes | Yes | No |
| Global | Can be secondary toa proximal MCA occlusion affecting bothsuperior and inferior division of the MCAa large superior division infarct that later becomes aBroca’s aphasialarge subcortical lesions such ashemorrhagesinfarcts | No | No | No |
| Transcortical motor | Can be secondary toan anterior cerebral artery (ACA)-MCA watershed infarct | No | Yes | Yes |
| Transcortical sensory | Can be secondary toa posterior cerebral artery (PCA)-MCA watershed infarct | Yes | No | Yes |
| Transcortical mixed | Can be secondary toboth an ACA-MCA and PCA-MCA infarct | No | No | Yes |