Snapshot
- A 15-year-old girl presents to the emergency room with a nosebleed that has not stopped for hours. She also has bleeding in her gums. She was recently started on carbamazepine for a newly diagnosed epileptic condition. Lab results reveal decreased counts in all leukocyte counts. Reticulocyte count is decreased as well. Carbamazepine is discontinued and a bone marrow biopsy is obtained.
Introduction
- Pancytopenia caused by diminished, absent, or destructed hematopoietic stem cells
- With bone marrow aplasia
- Epidemiology
- no racial or gender predisposition
- most cases are idiopathic – it is believed to be an autoimmune etiology
- Multiple different causes
- radiation
- drugs or chemicals
- benzene
- chloramphenicol
- anti-epileptics (phenytoin and carbamazepine)
- alcohol
- alkylating agents
- insecticides
- viruses
- EBV
- HIV
- CMV
- HCV
- parvovirus
- can cause transient aplastic crisis
- rarely can progress to aplastic anemia
- idiopathic
- B12 and folate deficiency
- PNH
- SLE
- PTU and methimazole
- Commonly seen in sickle cell patients who are infected with parvovirus B19
Presentation
- Symptoms/physical exam
- insidious onset, but often initial symptoms are due to anemia or bleeding
- (often normocytic) anemia: fatigue, malaise, and pallor
- thrombocytopenia: mucosal bleeding and petechiae
- leukopenia: infections
Evaluation
- Diagnosis of exclusion
- Labs
- anemia
- leukopenia
- thrombocytopenia
- ↓ reticulocyte count
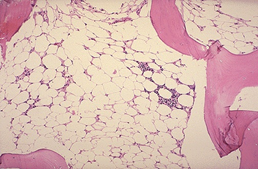
- Bone marrow biopsy
- hypocellular bone marrow with fatty infiltration
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- Withdrawal causative agent if applicable
- Supportive therapy
- RBC transfusion
- platelet transfusion
- Bone marrow transplant
- Antithymocyte globulin plus cyclosporine
- Hematopoietic growth factors (G-CSF and GM-CSF)
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- 10-year survival rate
- immunosuppression – 68%
- stem cell transplant – 73%
- 10-year survival rate
- Complications
- infection
- bleeding
- complications of stem cell transplant
- graft versus host disease


