Overview
Snapshot
- A 30-year-old woman presents to an asthma specialist for management of her moderate-to-severe asthma. She is currently using fluticasone and salmeterol inhalers. She continues to experience 2-3 episodes of asthma exacerbations a week with night-time awakenings and several trips to the emergency room in the past month. Her physician considers adding a targeted therapy that inhibits leukotrienes to her regimen.
Introduction
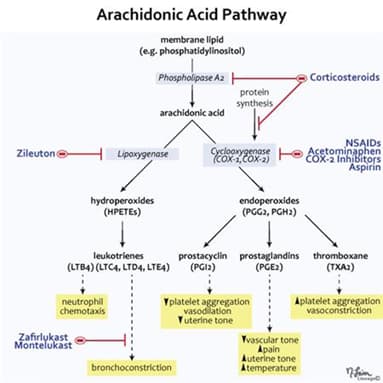
- Arachidonic acid pathway transforms arachidonic acid into a variety of inflammatory mediators, including leukotrienes, prostacyclin, and prostaglandins
- Many anti-inflammatory agents, including asthma medications, target downstream molecules in this pathway
- Lipoxygenase pathway products
- LTB4
- ↑ neutrophil chemotaxis
- LTC
4, LTD4, and LTE4- ↑ bronchial tone
- montelukast and zafirlukast inhibit these products
- LTB4
- Prostacyclin
- PGI2
- ↓ platelet aggregation
- vasodilation
- epoprostenol is a PGI2 analogue
- PGI2
- Prostaglandins
- PGE1
- vasodilation
- also known as alprostadil
- used to maintain a patent ductus arteriosus in newborns with ductal-dependent congenital heart disease
- PGE2
- ↑ uterine tone
- dinoprostone is a PGE2 analogue
- PGF2α
- ↑ uterine tone
- carboprost is a PGF2α analogue
- PGE1
- Thromboxane
- TXA2
- ↑ platelet aggregation
- ↑ vasoconstriction
- TXA2


