Overview
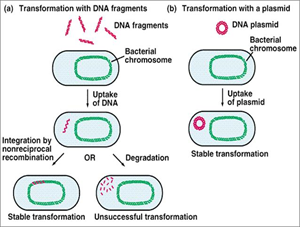
- the uptake of naked DNA from the environment
- any DNA can be used
- only bacteria that are “competent” are able to undergo transformation
- competence factor released by stressed bacteria induces this unique ability
- a feature of many bacteria
- especially S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae type B, Neisseria (“SHiN”)
- “having naked SHiNs was a transforming experience”
- Conjugation
- “bacterial sex”
- the major mechanism by which bacteria exchange plasmids
- allows the transmission of resistance to drugs
- F plasmid contains the genes required for conjugation
- F+ bacteria have the plasmid
- F– bacteria do not
- Hfr (“high frequency”) bacteria have incorporated the F plasmid into their chromosomal DNA
- F+ x F–
- plasmid is replicated inside F+ cell
- plasmid is transferred through pilus from F+ cell to F– cell
- only plasmid itself is transferred
- no transfer of chromosomal genes
- Hfr x F–
- plasmid and some flanking chromosomal DNA is replicated inside Hfr cell
- plasmid and some chromsomal DNA is transferred through pilus from F+ cell to F– cell
- in this case, both plasmid itself and chromosomal genes are transferred
- “a conjugal visit”
- Transduction
- transfer of bacterial DNA using virus (phage) as a carrier
- generalized transduction (“packaging”)
- lytic phage
- phage cleaves bacterial DNA
- parts of bacterial chromosomal DNA may become packaged in viral capsid
- DNA then travels in phage to infect another bacterium, transferring genes
- specialized (“excision”)
- lysogenic phage
- phage incorporates viral DNA into bacterial chromosome
- when phage DNA is excised from the bacterial chromosome, flanking bacterial genes may be excised with it
- DNA then travels in phage to infect another bacterium, transferring genes
- Transposition
- transposons (also known as insertion elements or transposable elements) are segments of DNA that can move from one location to another
- allows transfer of genes from plasmid to chromosome and vice-versa
- removal of a plasmid from the chromosomal DNA may include some flanking chromosomal DNA that may be transferred to another bacterium along with the plasmid


