Snapshot
- A 3-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician due poor growth and increased urinary frequency. According to the mother, the child appears to be very thirsty. He was born prematurely and the mother states she was found to have polyhydramnios on ultrasonograpahy while pregnant. Laboratory testing is significant for hypokalemia, hypochloremia, mild hypomagnesemia, and metabolic alkalosis.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- a renal tubular disorder characterized by
- hypokalemia
- hypochloremia
- metabolic alkalosis
- normotension
- elevated plasma renin level
- a renal tubular disorder characterized by
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- rare
- precise incidence is unknown
- demographics
- neonatal cases
- can be suspected before birth and diagnosed soon after birth
- classic cases
- begins around 2 years of age or younger
- no race or sex predilection
- neonatal cases
- risk factors
- family history
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- pathobiology
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal recessive
- inheritance pattern
- Prognosis
- can slowly progress to interstitial fibrosis resulting in chronic renal failure
Presentation
- Symptoms
- failure to thrive
- increased thirst
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- vomiting
- Physical exam
- clinical volume depletion
- maternal polyhydramnios
- growth retardation
Studies
- Labs
- ↑ plasma renin and aldosterone
- ↓ serum potassium and chloride
- ↑ urine prostaglandin E
- genetic testing
Differential
- Diuretic abuse
- Gitleman syndrome
- Surreptitious vomiting
- Mineralocorticoid excess
- Cystic fibrosis
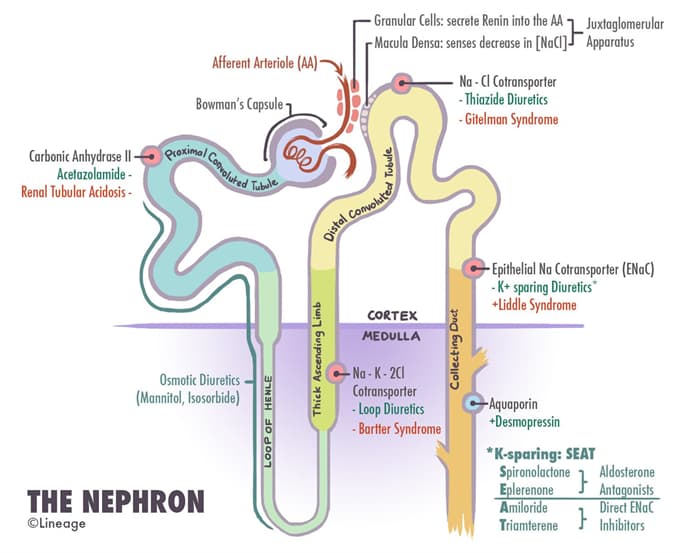
| Renal Tubular Defects | ||||
| Category | Fanconi Syndrome | Bartter Syndrome | Gitelman Syndrome | Liddle Syndrome |
| Defect localization | Proximal tubule | Thick ascending loop of Henle | Distal convoluted tubule | Collecting tubule |
| Etiology | Wilson diseaseTyrosinemiaCystinosisMultiple myelomaGalactosemiaMitochondrial myopathiesMedicationsaminoglycosidescisplatinifosfamidevalproic acidHeavy metalsmercury lead | Autosomal recessive mutation involving the NKCC2 cotransporter | Autosomal recessive mutation involving the Na+Cl– cotransporter | Autosomal dominant mutation leading to increased activity of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) |
| Findings | HypophosphatemiaAminoaciduriaRenal glucosuriaTubular proteinuriaProximal renal tubular acidosis | HypokalemiaHypochloremiaMetabolic alkalosisNormotensionElevated plasma renin level | HypokalemiaHypochloremiaMetabolic alkalosisHypomagnesemiaHypocalciuriaNormotension | HypertensionHypokalemiaMetabolic alkalosis |
Treatment
- Medical
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- indication
- for patients with Bartter syndrome
- drugs
- indomethicin
- celecoxib
- indication
- potassium-sparring diuretics
- indication
- to treat hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis in Bartter syndrome
- drugs
- spironolactone
- eplerenone
- amiloride
- indication
- potassium and magnesium supplementation
- indication
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- to help improve potassium and magnesium levels in Bartter syndrome
Complications
- Cardiac arrhythmia due to severe hypokalemia
Complications
- Cardiac arrhythmia due to severe hypokalemia


