Introduction
- The urinary organs consist of
- ureters (pelvic portion)
- carries urine from the kidney into the bladder
- urinary bladder
- the site of temporary urine storage
- urethra
- ureters (pelvic portion)
- the conduction site of urine from the urinary bladder to the external world
Ureters
- Muscular tubes that carries urine from the kidney into the bladder
- Blood supply consists of branches from
- renal arteries (most proximal)
- testicular arteries (in men) and ovarian arteries (in women)
- the descending aorta
- internal iliac arteries
- superior vesical arteries
- uterine arteries (in women)
- vaginal arteries (in women) and inferior vesical arteries (in men) (most distal)
Urinary Bladder
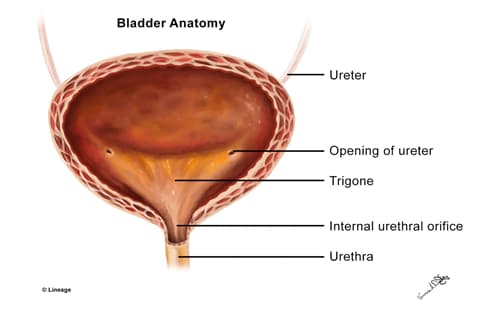
- A temporary reservoir of urine
- Innervation
- parasympathetic fibers
- conveyed from the sacral spinal cord via the pelvic splanchnic nerves and inferior hypogastric plexus
- provide motor innervation to the detrusor muscle
- inhibits contraction of the internal urethral sphincter in men
- sympathetic fibers
- conveyed from the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord via the hypogastric plexus and nerves
- parasympathetic fibers
- promotes contraction of the internal urethral sphincter
Urethra
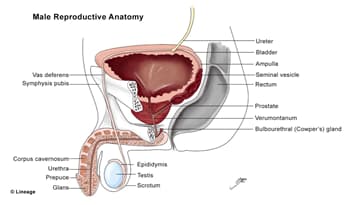
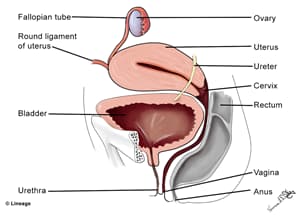
- A muscular tube that allows urine to travel from the urinary bladder to the external world
- the urethra also provides an exit path for semen
- Urethral injury
- posterior urethra
- the weakest point is in the bulbomembranous junction
- prone to injury in pelvic fractures (e.g., from a motor vehicle accident)
- can result in urine or blood being found in the retropubic space
- anterior urethra
- injury to the anterior urethra can result from
- straddle injuries
- instrumentation
- pelvic fracture (in conjunction)
- direct blow
- injury can result in urine or blood being found in the
- deep fascia of Buck
- superficial perineal space
- when the deep fascia of Buck is torn
- injury to the anterior urethra can result from
- posterior urethra


