Overview
Snapshot
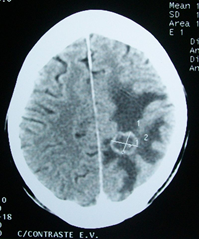
- A 56-year-old female is brought to the emergency department by her daughter due to new-onset abnormal movements suggestive of a seizure. While the patient is being managed, the physician learns that the patient is being treated for lung cancer. Head CT was obtained after the patient was stabilized.
Introduction
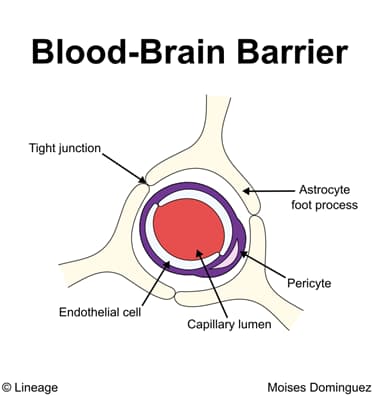
- Structure
- tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells
- also consists of astrocytic foot processes, pericytes, basement membrane
- irradiation, malignancy, infection can disrupt the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
- infarction destroys tight junctions → vasogenic edema
- fluid is extravasated into the interstitial space
- infarction destroys tight junctions → vasogenic edema
- tight junctions between nonfenestrated capillary endothelial cells
- Function
- control entry of substances into the brain
- substances cross via diffusion, ion channels, and selective transport proteins
- diffusion: nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances readily cross the BBB
- O2, CO2, heroin, nicotine
- ion channels: movement of Na+ and K+
- selective transport proteins: nutrients
- glucose, amino acids, peptides
- removes metabolites
- diffusion: nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances readily cross the BBB
- substances cross via diffusion, ion channels, and selective transport proteins
- certain areas of the CNS lack a BBB
- posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
- allows ADH release from brain into systemic circulation
- area postrema
- chemotherapeutic drugs → vomiting
- organum vasculosum lamina terminalis (OVLT)
- senses blood osmolality
- posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
- control entry of substances into the brain


