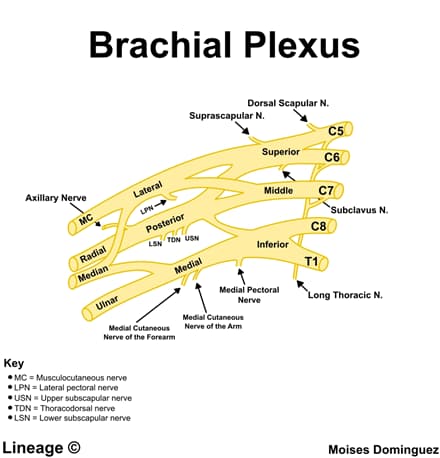
| Brachial Plexus Lesions |
| Plexopathy | Lesion Location | Etiology | Clinical Presentation |
| Erb palsy | C5-C6 roots negatively affects the deltoid and biceps brachii muscleC7 can occasionally be involved | Trauma leading to separation of the head and necke.g., lateral neck traction during birth delivery nfants—lateral traction on neck during delivery Adults—trauma | “Waiters tip”internal rotation, adduction, and extension of the armif C7 is involved there will be flexion of the wrist and fingersAtrophy and weakness of thedeltoidbiceps brachii |
| Klumpke palsy | C8-T1 roots negatively affects the intrinsic muscles of the hand | Upward force exerted on the arm when delivering a newborngrabbing a tree branch in an attempt to prevent a fall | “Claw hand”extension at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints and flexion at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) and PIP jointssecondary to impaired function of the lumbricals of the hand |
| Thoracic outlet syndrome | Compression of neurovascular structures in the thoracic outletclassically involved C8-T1 | Pancoast tumor Cervical rib | Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndromepain, numbness, and weakness in the affected nerves worsened when elevating the arms above the head (e.g., brushing hair) |
| Winged scapula | Long thoracic nervenegatively affects the serratus anterior muscle | Injury to the long thoracic nerveneuralgic amyotrophydirect trauma to the shoulder or lateral chest wall (e.g., playing football)surgerybreast surgery with axillary lymph node dissection | Projecting of the affected scapula while the patient presses against the wall |