Snapshot
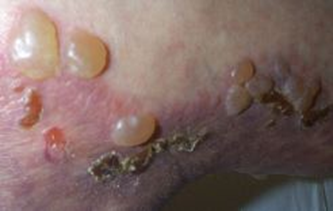
- A 75-year-old woman living in a nursing home presents with a 1-month history of severe pruritus. She reports having unrelenting pruritis with a pink rash over her trunk and extremities. Though she tried multiple lotions, the pruritus does not improve. Approximately 2 days ago, she also noticed some blisters on her body. She has never had rashes like this before. On physical exam, she has several 1-3 cm tense bullae on her abdomen and upper arms. Nikolsky sign is negative. A skin biopsy is taken and sent for immunofluorescence.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- more common in those > 70 years of age
- demographics
- Pathogenesis
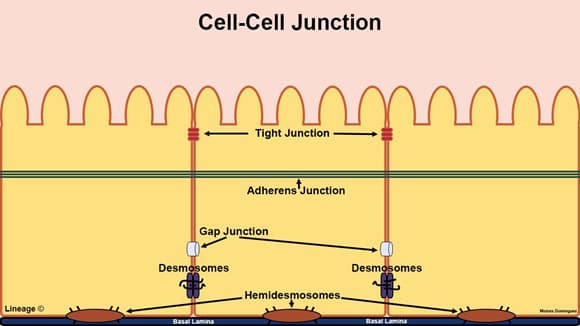
- auto-antibodies (IgG) against hemidesmosomes in the epidermal-dermal junction
- antibodies are below the epidermis
- main autoantigens are BP180 and BP230
- this activates complement and inflammatory reaction which cause epidermal-dermal splitting
- auto-antibodies (IgG) against hemidesmosomes in the epidermal-dermal junction
- Associated conditions
- drug use
- loop diuretics
- metformin
- neuroleptics
- neurologic conditions
- multiple sclerosis
- dementia
- Parkinson disease
- drug use
- Prognosis
- can resolve spontaneously
- often recurs
Presentation
- Symptoms
- severe pruritus
- may have history of eczematous or urticarial lesions before bullae formation
- Physical exam
- tense bullae with clear exudate
- may be hemorrhagic
- typically symmetrically distributed on trunks and extremities
- spares mucous membranes
- negative Nikolsky sign
- cannot cause separation, blister formation, or blister extension with blunt pressure or lateral traction (dragging finger on skin)
- tense bullae with clear exudate
- may have vesicles
Studies
- Labs
- autoantibodies in serum detected with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- for monitoring disease activity
- anti-BP180 antibodies
- anti-BP230 antibodies
- autoantibodies in serum detected with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Histology
- subepidermal blister with eosinophils
- direct immunofluorescence
- linear pattern of IgG and C3 deposition along the epidermal-dermal junction
Differential
Treatment
- Conservative
- discontinue new medications
- indications
- if BP is suspected to be a drug reaction
- indications
- wound care
- indications
- all patients
- antiseptic care for erosions
- indications
- discontinue new medications
- Medical
- topical corticosteroids
- indications
- first-line treatment
- often used with systemic treatments
- drugs
- clobetasol
- indications
- prednisone
- indications
- for widespread disease or if topical steroids are not feasible
- indications
- steroid-sparing immunosuppressant
- indications
- for those contraindicated to steroids
- drugs
- indications
- topical corticosteroids
- azathioprine
Complications
- Skin and soft tissue bacterial infection of open lesions


