Definitions and Concepts
- Growth fraction
- high growth fraction means large percentage of cells are actively dividing
- cytotoxic drugs are more deadly against
- high growth fraction tumors
- leukemias
- lymphomas
- normal cells with high growth fraction
- bone marrow
- GI
- high growth fraction tumors
- Cell-cycle specificity
- cell-cycle specific drugs
- act only during certain phases of the cell cycle
- more effective against high-growth fraction tumors
- cell-cycle nonspecific drugs
- used in both high- and low-growth fraction tumors
- cell-cycle specific drugs
- Log-kill hypothesis
- cytotoxic drugs kill a fixed percentage of tumor cells
- not a fixed number
Cell Cycle
- S phase
- agents binding to DNA
- alkylating agents
- anti-tumor antibiotics
- platinum compounds
- antimetabolites
- methotrexate
- azathioprine
- 6-MP
- 5-FU
- agents binding to DNA
- M phase
- microtubule inhibitors
- vinca alkaloids
- paclitaxel
- microtubule inhibitors
Sites of Action
| Mechanism of Action | Drugs | Mechanism |
| Nucleotide synthesis | Methotrexate 5-FU | ↓ thymidine synthesis |
| 6-MP | ↓ purine synthesis | |
| DNA | Alkylating agents Cisplatin | Cross-link DNA |
| Dactinomycin Doxorubicin | Intercalate DNA | |
| Etoposide | Inhibit topoisomerase II | |
| Cellular division | Vinca alkaloids | Inhibit MT formation |
| Paclitaxel | Inhibit MT disassembly |
Important Toxicities
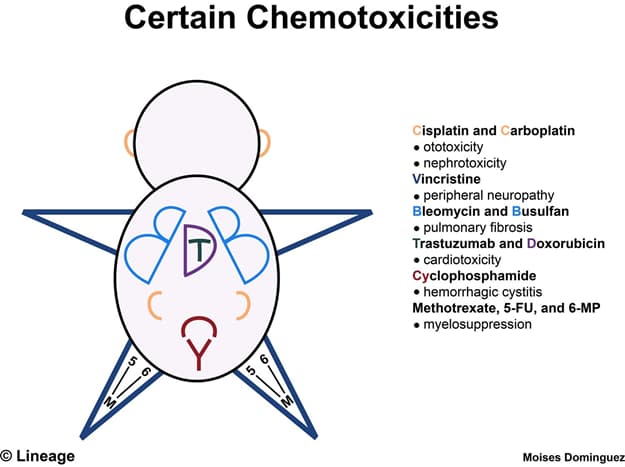
| Drugs | Toxicities |
| Bleomycin | Pulmonary fibrosis |
| Cisplatin and Carboplatin | Acoustic nerve damage and nephrotoxicity |
| Cyclophosphamide | Hemorrhagic cystitis |
| Doxorubicin | Cardiotoxicity |
| Methotrexate, 5-FU, and 6-MP | Myelosuppression |
| Vincristine | Peripheral neuropathy |
Development of resistance
- Tumors can develop resistance to anticancer drugs through a variety of mechanisms
- ↓ sensitivity/affinity
- etoposide
- methotrexate
- vinblastine and vincristine
- ↓ accumulation
- methotrexate
- alkylating agents
- dactinomycin
- ↑ drug-inactivating enzymes
- antimetabolites of purine and pyrimidine
- ↑ trapping of drug
- alkylating agents
- bleomycin
- cisplatin
- doxorubicin
- ↑ DNA repair
- alkylating agents
- cisplatin
- ↓ bioactivation
- antimetabolites of purine and pyrimidine
- ↓ sensitivity/affinity
- Combination drug regimens prevent the development of resistance


