Introduction
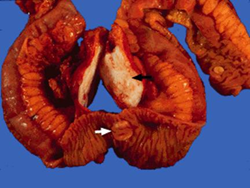
- Tumor of neuroendocrine origin
- most common small bowel tumor
- Location
- most common sites are the rectum and stomach
- these foregut and hindgut masses rarely metastasize
- most common site of metastatic primary mass is terminal ileum
- appendix is common tumor site but too small to metastasize
- most common sites are the rectum and stomach
- Pathophysiology
- often produce 5-HT ectopically
- can lead to carcinoid syndrome
Evaluation
Treatment
- Pharmacologic
- hormone therapy
- somatostatin analogue to prevent extra hormones from being produced
- octreotide or lanreotide can help lessen flushing and diarrhea
- radiation and chemotherapy
- hormone therapy
- Surgical
- surgical resection
- can be done endoscopically, with local excision or with cryosurgery
- surgical resection


