Overview
Snapshot
- A 45-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician’s office due to pain in her hand. The patient reports that the pain is worse at night and when her hand is outstretched. Her symptoms are also accompanied by paresthesias in the affected hand. She denies any recent injury to or pain in the hand or neck. She works as a secretary at a medical clinic. On physical exam, she has a positive Phalen and Tinel test.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- compressive median nerve neuropathy
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- bimodal distribution of age
- 50-60 and 70-80 years of age
- bimodal distribution of age
- risk factors
- female gender
- obesity
- pregnancy
- hypothyroidism
- rheumatoid arthritis
- dialysis-related amyloidosis
- demographics
dialysisrelated
amyloidosis
- repetitive use of the hand or wrist
- Etiology
- increased pressure within the carpal tunnel
- Pathoanatomy
- borders
- floor: proximal carpal row
- laterally: scaphoid and trapezium
- medially: hook of hamate and pisiform
- normal anatomy
- the carpal tunnel contains
- digital flexor tendons
- flexor pollicis longus tendon
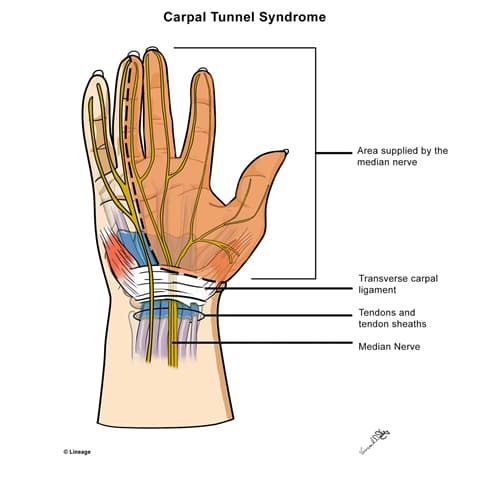
- median nerve
- the carpal tunnel contains
- pathology
- synovial noninflammatory fibrosis and thickening leads to median nerve compression (most common)
- compression leads to microvascular insufficiency causing ischemic damage to the nerve
- borders
- Prognosis
- in mild-to-moderate cases, there is spontaneous resolution or response to conservative therapy
Presentation
- Symptoms
- pain or paresthesia in the median nerve distribution
- median nerve distribution
- the first 3 digits and radial half of 4th digit
- symptoms typically worse at night
- median nerve distribution
- weakness or hand clumsiness
- pain or paresthesia in the median nerve distribution
- Physical exam
- pain and/or paresthesia in the median nerve distribution is a positive test
Studies
- Making the diagnosis
- the diagnosis can be clinically made; however, it is confirmed by nerve conduction studies
- Nerve conduction studies
- indication
- may be used when contemplating surgical decompression
- indication
- Electromyogram
- indication
- typically used to exclude other etiologies such as
- polyneuropathy
- plexopathy
- typically used to exclude other etiologies such as
- indication
- radiculopathy
Differential
- Cervical radiculopathy compressing C5-C6
- distinguishing factors
- patients have neck pain, worsening symptoms with head movement, and pain radiation to the shoulders and arm
- distinguishing factors
- patients also have reduced biceps, brachioradialis, and triceps reflex
Treatment
- Conservative
- splinting
- indication
- to improve mild carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms
- indication
- splinting
- Medical
- corticosteroid (oral or injection)
- indication
- to improve mild carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms
- indication
- corticosteroid (oral or injection)
- Operative
- surgical decompression
- indication
- for severe median nerve injury
- indication
- surgical decompression
- reflected by nerve conduction studies (e.g., severe axonal degeneration) or needle electromyography
Complications
- Rare


