Overview
Introduction
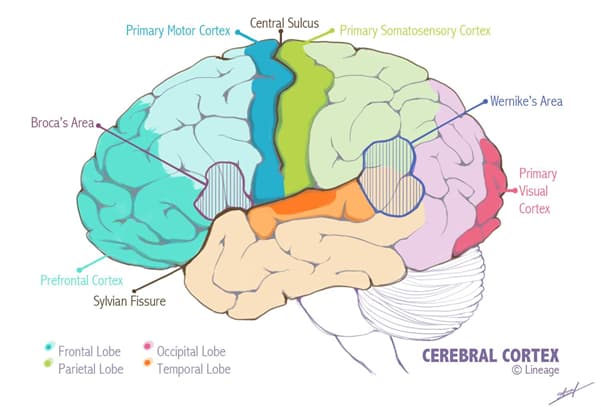
- Anatomy
- the cerebral cortex contains eminences (termed gyri) and spaces separating these eminences (termed sulci)
- sulci include
- lateral (Sylvian) fissure
- separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobe
- central sulcus
- separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
- note that anterior to this sulci is the precentral gyrus and posterior to the this sulci is the postcentral gyrus
- the precentral gyrus is the primary motor cortex
- the postcentral gyrus is the primary somatosensory cortex
- parieto-occipital sulcus
- which separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe and can best be seen medially
- calcarine sulcus
- which separates the cuneus from the lingual gyrus
- lateral (Sylvian) fissure
- the lobes of the cerebral cortex includes
- frontal lobe
- primary motor cortex and premotor cortex are involved in
- contralateral movement
- frontal eye fields are involved in
- eye movement
- prefrontal cortex is involved (this is a simplification) in
- restraint
- initiative
- order
- primary motor cortex and premotor cortex are involved in
- parietal lobe
- primary somatosensory cortex is involved in
- receiving contralateral sensory information
- Wernicke area (junction of parietal and temporal lobes) is involved in
- language comprehension
- primary somatosensory cortex is involved in
- temporal lobe
- primary auditory cortex is involved in
- processing sound
- primary auditory cortex is involved in
- occipital lobe
- visual and visual association cortex is essential for
- receiving and recognizing visual stimuli
- visual and visual association cortex is essential for
- frontal lobe
- sulci include
- the cerebral cortex contains eminences (termed gyri) and spaces separating these eminences (termed sulci)
- Blood supply
- the brain receives blood from the internal carotid and vertebral arteries
- anastomoses of the internal carotid arteries and basilar artery results in the formation of the
- circle of Willis
- anastomoses of the internal carotid arteries and basilar artery results in the formation of the
- the blood supply will be simplified as follows
- middle cerebral artery
- supplies blood to most of the lateral surface of the brain as well as the
- posterior limb and genu of the internal capsule
- supplies blood to most of the lateral surface of the brain as well as the
- anterior cerebral artery
- supplies the medial surface of the parietal and frontal lobe as well as the
- anterior limb of the internal capsule
- supplies the medial surface of the parietal and frontal lobe as well as the
- posterior cerebral artery
- supplies the occipital lobes
- middle cerebral artery
- the brain receives blood from the internal carotid and vertebral arteries


