Overview
Snapshot
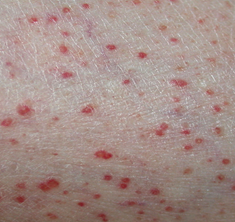
- A 22-year-old male presents with altered mental status, fever, and headache. The patient is able to sluggishly answer questions. Passive flexion of the neck leads to spontaneous contraction of the hips. Pain is elicited when attempting to fully extend the knee while his hips are at a 90 degree angle. A skin finding is shown to the right.
Introduction
- Function
- serves as a mechanical cushion for the CNS
- protects the brain against concussive injury
- removal of metabolites
- CSF flow is one-way
- hormone and hormone-releasing factor transportation
- homeostasis
- CSF pH affects ventilation and cerebral blood flow
- serves as a mechanical cushion for the CNS
- Production
- produced by the choroid plexus epithelial cells within ventricles
- found in lateral, third, and fourth ventricles
- reabsorbed into circulation by arachnoid granulations
- enters dural venous sinuses
- entire volume of CSF is recycled 2-3 times per 24 hours
- produced by the choroid plexus epithelial cells within ventricles
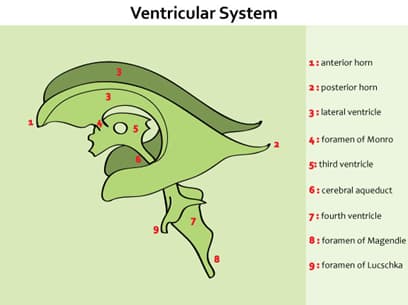
- Ventricular system communications
- 3rd ventricle → 4th ventricle
- via the cerebral aqueduct (Aqueduct of Sylvius)
- 4th ventricle → subarachnoid space via
- foramina of Luschka (lateral)
- foramen of Magendie (medial)
- 3rd ventricle → 4th ventricle
- Compared to the serum:
- ↓↓ protein
- ↓ glucose
- ↓ pH
- ↓ K+, HCO3–, Ca2+
- ↑ Cl-, Mg2+
Presentation
| Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis | |||
| Test | Normal | Bacterial | Viral |
| Opening pressure | ≤ 20 cm H 2O | ↑ | normal or slightly ↑ |
| Color | Clear | Cloudy | Clear |
| Cell count | 0-5 cells/µL | ↑ (PMN) | ↑ (Lymphocytes) |
| Protein | < 45 mg/dL | ↑ | Slighty ↑ |
| CSF:Serum glucose | > 0.6 | ↓ | Normal |
- Hydrocephalus
- dilated ventricles via several types
- communicating
- ↓ reabsorption of CSF
- scarring of arachnoid granulations following meningitis
- ↑ production of CSF (rare)
- choroid plexus papilloma
- ↓ reabsorption of CSF
- noncommunicating/obstructive
- obstructed flow of CSF
- stenosis at narrow point along ventricular system
- e.g., at the cerebral aqueduct, foramen of Monro
- Chiari II malformation
- Dandy-Walker syndrome
- stenosis at narrow point along ventricular system
- obstructed flow of CSF
- normal pressure (NPH)
- ex vacuo
- communicating
- dilated ventricles via several types



