| Artery | Syndrome | Presentation |
| Anterior Spinal artery | Medial medullary syndrome | Ipsilateral paralysis of hypoglossal nerve Contralateral hemiparesis of the upper and lower extremityMedial lemniscus (↓ contralateral vibration and proprioception) |
| Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) | Lateral medullary syndrome | Ipsilateral manifestationsfacial loss of pain and temperatureataxia (arm and leg, gait)hoarsenessdysphagiaHorner syndromeContralateral manifestationspain and temperature hemisensory lossNausea, nystagmus, vomiting, vertigo |
| Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) | Lateral pontine syndrome | Ipsilateral manifestationsfacial paralysisloss of lacrimationreduced salivationloss of corneal reflexloss of sensation of the anterior 2/3rd of the tongueHorner syndromesensorineural hearing lossloss of facial pain and temperatureContralateral manifestationspain and temperature hemisensory loss |
| Posterior cerebral artery | – | Contralateral homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing |
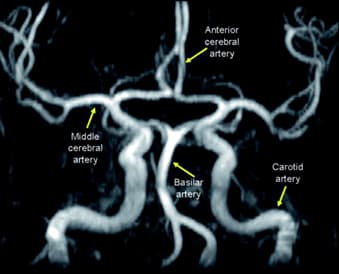
| Middle cerebral artery | – | Contralateral manifestationsfacial paralysis and sensory lossupper extremity weakness and sensory losshemineglect (if stroke is in non-dominant hemisphere)aphasia (if stroke is in dominant hemisphere-Broca’s area) |
| Anterior cerebral artery | – | Contralateral manifestationslower extremity weakness and sensory loss |
| Posterior communicating artery | – | Ipsilateral compression leading to CN III palsydown-and-out, mydriasis |
| Lenticular striate artery | – | Contralateral manifestationsmotor hemiparesishemisensory lossLack of cortical signsno aphasia, neglect |
| Basilar artery | Locked-in syndrome | QuadriplegiaPreserved reticular formationIntact vertical eye movementIntact blinking |
| Anterior communicating artery | – | Can compression of optic chiasmbitemporal hemianopiaIf rupture, ischemia in anterior cerebral artery territory |