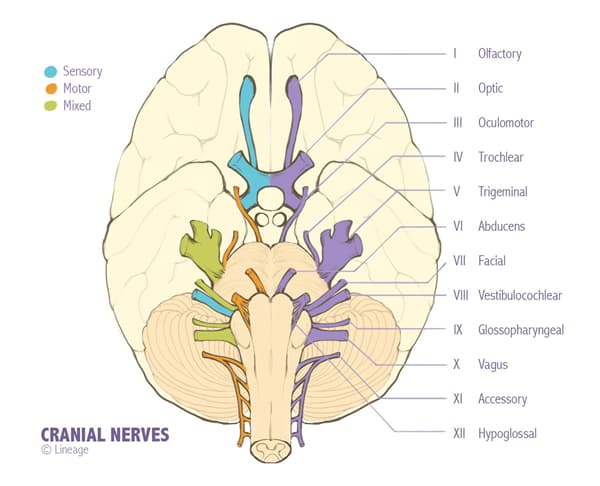
| Cranial Nerves |
| Cranial Nerve | Type | Function | Cranial Exit | Notes |
| Olfactory nerve (I) | Sensory | Olfaction | Cribiform plate | Only CN without thalamic relay to the cortex Cribiform plate fracture can lead to anosmia |
| Optic nerve (II) | Sensory | Vision | Optic canal | – |
| Oculomotor nerve (III) | Motor | Eye movement via thesuperior, inferior, and medial rectusinferior oblique musclePupillary constrictionAccomodationEyelid opening via innervation of thelevator palpebrae muscle | Superior orbital fissue | Center contains output to ocular muscles which is affected primarily 1st by vascular diseasePeriphery contains parasympathetic output which is affected 1st by compression |
| Trochlear nerve (IV) | Motor | Eye movement via innervation of thesuperior oblique muscle | Superior orbital fissue | – |
| Trigeminal nerve (V) | Motor and sensory | Mastication via the mandibular nerve (V3) Facial sensation via the ophthalmic nerve (V1)maxillary nerve (V2)mandibular (V3) | Ophthalmic nerve (V1)superior orbital fissureMaxillary nerve (V2)foramen rotundum Mandibular nerve (V3)foramen ovale | Mediates the jaw jerk reflex |
| Abducens nerve (VI) | Motor | Eye movement via innervation of thelateral rectus | Superior orbital fissure | – |
| Facial nerve (VII) | Motor and sensory | Facial movementTaste from the anterior 2/3 of tongueLacrimationSalivation via innervation of thesubmandibular glandsublingual glandEyelid closing via innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscleStapedius dampens excessive sound | Internal auditory meatus | Visceral sensation recieved by nucleus solitarius |
| Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) | Sensory | HearingBalance | Internal auditory meatus | – |
| Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) | Motor and sensory | Taste from posterior 1/3 of tongueSwallowingSalivation parotid glandMonitoring carotid body and sinus chemo- and baroreceptorsStylopharngeuselevates pharynx and larynx | Jugular foramen | Motor output orginates in nucleus ambiguusVisceral sensation recieved by nucleus solitarius |
| Vagus nerve (X) | Motor and sensory | Taste from epiglottic regionSwallowingPalate elevationMidline uvulaTalkingCoughingThoracoabdominal visceraMonitoring aortic arch chemo- and baroreceptorsCan cause vasovagal syncope in response to an emotional stimulus | Jugular foramen | Motor output orginates in nucleus ambiguusVisceral sensation recieved by nucleus solitariusParasympathetic fibers to heart, lungs, and upper GI orginates from dorsal motor nucleusGives recurrent laryngeal nerve which innervates all laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid |
| Accessory nerve (XI) | Motor | Head turning and shoulder shruggingsternocleidomastoid muscletrapezius | Jugular foramen | Motor output orginates in nucleus ambiguus |
| Hypoglossal nerve (XII) | Motor | Tongue movement | Hypoglossal canal | – |