Snapshot
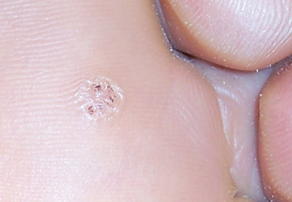
- A 55-year-old man presents to his dermatologist for plantar warts. While the lesions do not hurt on its own, they are painful when he wears exercise sneakers or exercises. He reports that he has only one but is scared of it spreading. Physical exam reveals a single 3-mm flesh-colored papule with a thick scale. The striae of his plantar surface wind around the lesion. Cryotherapy is done in the office.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- children and young adults
- risk factors
- atopic dermatitis
- immunosuppression
- walking barefoot in communal swimming areas
- occupations
- handlers of meat and fish
- demographics
- Etiology
- HPVs
- over 150 subtypes
- HPVs
- Pathogenesis
- transmitted through contact with infected skin of mucous membranes
- warts contain high viral load
- virus invades epidermal basal layer through microabrasions and are confined to epidermis
- incubation period is 2-6 months
- transmitted through contact with infected skin of mucous membranes
- Prognosis
- often spontaneously resolves in children
- often require several sessions of treatment in adults
Presentation
- Symptoms
- asymptomatic
- commonly appear at sites of trauma
- Physical exam
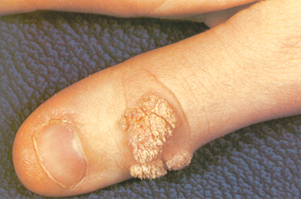
- commonwarts
- flesh-colored papules
- can be
- cauliflower-shaped
- smooth
- black dots (thrombosed capillaries) when pared with a surgical blade
- hands are most commonly involved
- flat warts
- pink, light brown, or light yellow flat-topped papules
- most commonly on mouth and forehead
- plantar warts
- on plantar surface of feet, often at points of maximum pressure
- accompanied with thick callus
- striae (natural lines of skin) often avoid the lesion
- single or grouped lesions
- warts on adjacent toes
- commonwarts
- “kissing lesions”
Studies
- Biopsy
- indications
- if diagnosis is unclear
- indications
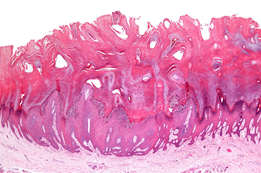
- Histology
- epidermal hyperplasia
- hyperkeratosis
- koilocytosis
- Making the diagnosis
- a clinical diagnosis
Differential
Treatment
- Medical
- destruction of warts
- indications
- cosmetic reasons
- associated pain or irritation
- immunosuppression
- modalities
- topical salicylic acid
- first-line
- cryotherapy
- because of pain, usually used in older children or adults
- topical cantharidin
- laser
- topical salicylic acid
- indications
- topical immunotherapy
- indication
- refractory to first-line treatment
- modalities
- squaric acid dibutylester
- dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)
- indication
- destruction of warts
- diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP)
Complications
- No significant complications


