Snapshot
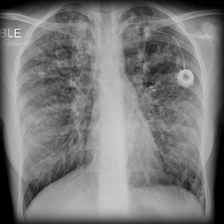
- A 3-year-old boy with a history of recurrent pneumonia and chronic diarrhea. His mother states that he has 6-8 four smelling stools per day. PE reveals a low grade fever, scattered rhonchi over both lung fields, crepitant rales at the left lung base and dullness to percussion.
Introduction
- Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder leading to excessive, viscous secretions that plug exocrine glands
- autosomal recessive disorder
- caused by mutations in CFTR gene (chloride channel) on chromosome 7
- CFTR is a transmembrane cAMP-activated ion channel
- its normal function is to reabsorb chloride ions (lumen → cell) in sweat glands and to secrete chloride ions (cell → lumen) in other exocrine glands (e.g., pancreas and lungs)
- movement of chloride creates a charge gradient that induces movement of sodium ions in the same direction as chloride to mitigate the gradient
- movement of these ions drags solvent (water) with them
- CFTR is a transmembrane cAMP-activated ion channel
- Affects multiple organ systems with widespread exocrine gland dysfunction
- pancreatic exocrine insufficiency is responsible for most of them
- Epidemiology
- most common genetic disease in the United States
- mostly affects Caucasians
- Newborn screening now routine in all states
Presentation
- Symptoms
- respiratory symptoms are more prominent in adulthood
- recurrent pulmonary infections
- Pseudomonal spp and S. aureus are most common
- chronic sinusitis
- chronic, productive cough
- dyspnea on exertion
- hemoptysis
- recurrent pulmonary infections
- gastrointestinal symptoms are more prominent in infancy
- chronic, frequent diarrhea
- greasy stool with flatulence from malabsorption secondary to pancreatic insufficiency
- steatorrhea can cause deficiency in fat soluble vitamins
- can lead to rectal prolapse
- meconium ileus in infants (15%)
- pancreatitis
- chronic, frequent diarrhea
- respiratory symptoms are more prominent in adulthood
- Physical exam
- failure to thrive (50%)
- respiratory compromise (50%)
- “salty taste”
- cyanosis
- digital clubbing
- ronchi
- rales
- hyperresonance of chest to percussion
- nasal polyposis
Evaluation
- CXR
- hyperinflation
- prominent bronchovascular markings
- bronchiectasis with “tram tracks” and peribronchial cuffing
- diffuse bronciectactic changes
- Sweat chloride test
- historical diagnostic gold standard
- >60 mEq/L in patients <20 years old
- >80 mEq/L in adults
- Genetic testing
- confirms disease by identification of specific genetic mutation
- Immunoreactive trypsinogen assay
- Nasal transepithelial potential difference
- Pulmonary function testing
- often abnormal before first birthday
- obstructive pattern with increased lung volumes (TLC and RV) over time from air trapping and hyperinflation
- reduced diffusing capacity (DLCO)
- reduced or normal FEV1:FVC ratio given obstructive pattern with possible late restrictive features (e.g., fibrosis, tissue destruction, and/or hyperinflation)
Differential
- Inherited immunodeficiency (SCID, CVID)
- Primary ciliary dyskinesia
Treatment
- Lifestyle
- health maintenance
- nutritional counseling
- psychiatric/psychologic support indicated in most patients with or without mental instability
- up-to-date immunizations indicated in all patients
- health maintenance
- Pharmacologic
- respiratory therapy
- indicated in all patients
- includes several components including
- chest physiotherapy (percussion, positive pressure, nebulizers)
- bronchodilators
- inhaled corticosteriods
- if asthmatic component or ABPA
- DNA-ase and hypertonic saline
- antibiotics
- chronic macrolide therapy common
- IV antibiotics for acute exacerbations
- anti-inflammatory agents (ibuprofen)
- pancreatic enzymes and fat-soluble vitamins
- indicated for malabsorption
- respiratory therapy
- Operative
- lung and pancreas transplantation
- indicated for most severe, but only if patient can tolerate surgery
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- while patients are living longer and more complete lives with modern medicine, rarely do CF patients live beyond 40 years of age without transplantation
- Prevention
- immunization for influenza and pneumococcus can prevent infections
- embryonic selection, although controversial, has been used by known carriers or affected couples to prevent transmission of the disease to their children
- Complications
- chronic hypoxemia and hypercapnia lead to pulmonary hypertension
- patients often develop cor pulmonale (RHF)
- idiopathic hyponatremia
- CF-related diabetes mellitus
- esophageal varices
- biliary cirrhosis and cholelithiasis
- chronic hypoxemia and hypercapnia lead to pulmonary hypertension



