Overview
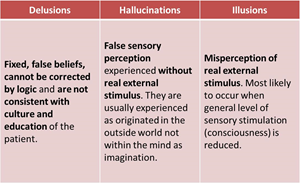
- Delusions
- false beliefs firmly maintained in spite of indisputable and obvious proof to the contrary
- not shared with other members of patient’s culture/subculture
- e.g. thinking the CIA is spying on you
- false beliefs firmly maintained in spite of indisputable and obvious proof to the contrary
- Hallucinations
- perceptions in the absence of external stimuli
- e.g. hearing sound when no sound is present
- Illusions
- misinterpretations of actual external stimuli
- e.g. hearing the wind blowing and thinking it is a bird chirping
- Loose associations
- ideas are presented with illogical or tenuous connections between them
Hallucination types
- Visual hallucinations
- common in delirium
- more often a feature of medical rather than psychiatric illness
- Auditory hallucinations
- common in schizophrenia
- more common in psychiatric than medical disease
- Olfactory hallucinations
- often occurs as an aura of psychomotor epilepsy or brain tumors
- Gustatory hallucination
- rare
- Tactile hallucinations
- Hypnagogic hallucination
- occurs while going to sleep
- Hypnopompic hallucination
- occurs while waking from sleep


