Disease Prevention: Individual Level
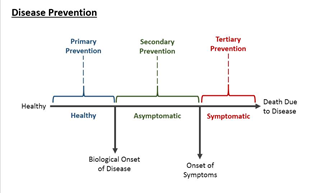
- 1° (Primary prevention)
- prevent disease occurrence
- e.g., vaccination
- prevent disease occurrence
- 2° (Secondary prevention)
- early detection of disease to either prevent or decrease morbidity from disease before onset of symptoms
- e.g., colonoscopy
- early detection of disease to either prevent or decrease morbidity from disease before onset of symptoms
- 3° (Tertiary prevention)
- reduce morbidity from disease after symptom onset
- e.g., medication
- reduce morbidity from disease after symptom onset
- 4° (Quaternary prevention)
- reducing harm by identifying patients who are at risk for unnecessary treatment, overmedicalisation, harm from new interventions, and suggest new interventions which are ethically acceptable
- e.g., not spending money on things that do not work or recommendation of preventive measures of proven efficacy
Disease Prevention: Health Promotion
- Also known as primordial prevention
- Prevention at the community level involves promoting the health of entire populations and avoiding health risks altogether
- Social and economic policy-making
- cigarette, soda, or other taxes
- smoke-free cities, buildings, and restaurants
- investments in public transportation and schools
- Health education
- public health campaigns surrounding smoking, alcohol, diet, and exercise
- Environmental interventions
- promoting green space
- reducing pollution
- Addressing health care disparities


