Snapshot
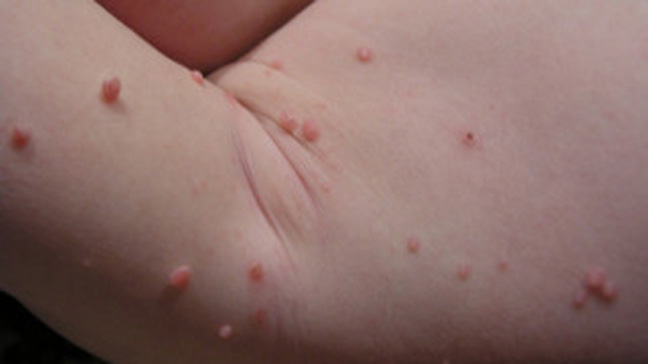
- A 17-year-old patient presents to your clinic with a
new rash. He is a wrestler on his high school varsity team. The rash is mildly itchy, but the patient denies any oozing or bleeding. On exam, you note umbilicated, waxy spots along his neck, arms, and waist in a nonspecific pattern. What are the characteristics of the most likely virus affecting this patient?
DNA Virus Table
Introduction to Viruses
- Viruses are obligate intracellular infectious agents with the following basic components
- DNA or RNA
- never both
- capsid
- a protein coat that surrounds the genetic material
- icosahedral or helical symmetry
- made of capsomers
- polypeptide chains organized into a globular subunit
- in helical symmetry, capsomers are bound to RNA and coiled
- forms a helical nucleoprotein capsid
- sometimes an envelope
- DNA or RNA
- Viruses are classified by
- nucleic acid
- DNA or RNA
- double stranded or single stranded
- (+) positive or (-) negative stranded RNA
- single or segmented pieces of nucleic acid
- complexity of genome
- capsid
- icosahedral or helical
- envelope
- naked
- DNA or RNA + capsomers and other structural proteins = nucleocapsid (no host membrane)
- enveloped
- nucleocapsid + host membrane with viral-specified glycoproteins = enveloped virus
- naked
- size
- diameter or number of capsomers
- ploidy
- all viruses are haploid (1 copy of DNA or RNA)
- except retroviruses
- retroviruses have 2 identical copies of their ssRNA, approximating diploidy
- infectivity of purified nucleic acid
- purified nucleic acid that is intrinsically infectious
- dsDNA from most viruses
- except poxviridae
- except HBV
- (+) ssRNA from most viruses
- (+) linear, nonsegmented ssRNA can be translated immediately into a large protein by host machinery
- virus must carry protease to cleave the 1 large protein product that will be generated by the host machinery
- dsDNA from most viruses
- purified nucleic acid that is NOT intrinsically infectious
- (-) ssRNA
- viruses must carry an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase to generate mRNA the host machinery can read
- dsRNA
- (-) ssRNA
- purified nucleic acid that is intrinsically infectious
- nucleic acid
- they require enzymes contained in the complete virion for infectivity
DNA Viruses
- Most DNA viruses
- are double-stranded (dsDNA, like human DNA)
- have icosahedral symmetry
- replicate in the nucleus
- are linear
- Exceptions
- parvoviridae
- only 1 strand of DNA (ssDNA)
- poxviridae
- no icosahedral symmetry
- surrounded by complex structural proteins
- replicates in cytoplasm
- no icosahedral symmetry
- papilloma, polyoma, and hepadna
- are non-linear (circular)
- parvoviridae
- Enveloped vs naked
- 3 DNA viruses are enveloped
- herpes
- hepadna
- pox
- the rest are naked
- 3 DNA viruses are enveloped
- The DNA viruses are “HHAPPPPy”
- herpes
- hepadna
- adeno
- pox
- polyoma
- papilloma
- parvo


