Overview
- Elimination of drugs
- rate of elimination is rate of disappearance of active molecules from bloodstream or body
- rate of elimination and dosage determine duration of action of a drug
- drug elimination ≠ drug excretion
- e.g., a drug may be eliminated by metabolism before excretion from body
Zero-order elimination
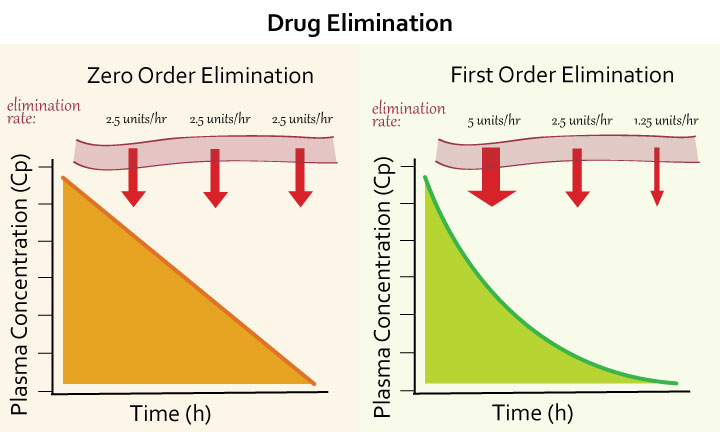
- Zero-order elimination
- implies rate of elimination is constant, regardless of drug concentration
- constant amount of drug is eliminated per unit time
- drug concentration in plasma (Cp) decreases linearly with time
- e.g., phenytoin, ethanol, aspirin
- implies rate of elimination is constant, regardless of drug concentration
- aspirin is zero-order drug at high therapeutic or toxic concentrations
First-order elimination


