Corrosive Esophagitis
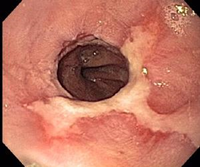
- Caused by ingestion of strongly acidic or basic chemical
- Lye, HCl
- Results in
- esophageal perforation
- esophageal stricture formation
Infectious Esophagitis
- Commonly seen in AIDS patients
- May be viral or fungal
- HSV-1
- mutiple punched-out ulcers throughout esophagus with normal mucousa
- ulcers can coalese and form “black esophagus”
- histology will show eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (Cowdry type A) and multinucleated squamous cells surrounding the ulcers on biopsy
- mutiple punched-out ulcers throughout esophagus with normal mucousa
- CMV
- single, large, shallow, linear ulcer
- HSV-1
- Odynophagia is main symptom


