Overview
Introduction
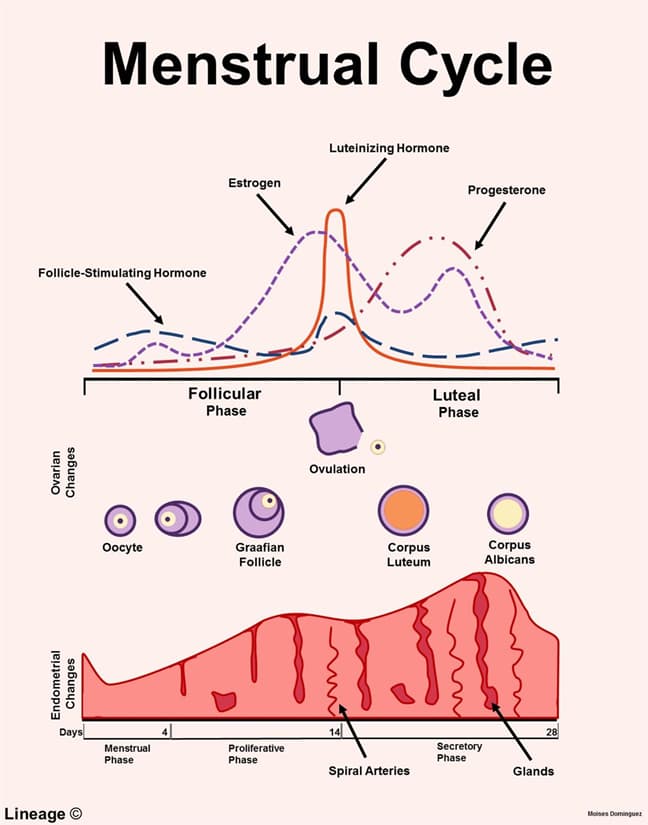
- Female hormones
- in follicular phase of menstrual cycle, follicle synthesizes estrogens
- major product is 17β-estradiol
- in luteal phase of menstrual cycle, corpus luteum synthesizes progesterone and estrogen
- in follicular phase of menstrual cycle, follicle synthesizes estrogens
- major product is progesterone
Estrogen
- Sources of estrogens
- ovary (17β-estradiol)
- placenta (estriol)
- blood (aromatization)
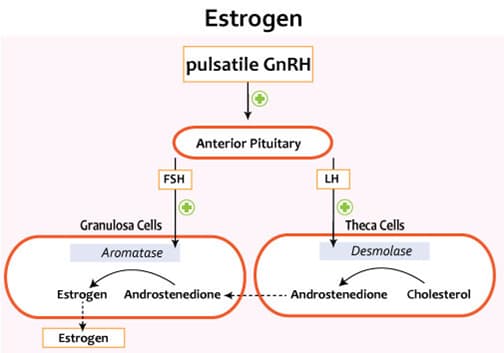
- Estrogens biosynthesis
- two-cell, two-gonadotropin model
- 17β-estradiol synthesis requires granulosa cells and theca cells
- theca cells do not express aromatase
- aromatase catalyzes conversion of androstenedione to 17β-estradiol
- theca cells do not express aromatase
- biosynthetic pathway
- LH acts on theca cells
- increases activity of cholesterol desmolase
- increases synthesis/secretion of androstenedione
- androstenedione freely diffuses from theca cells to granulosa cells
- increases activity of cholesterol desmolase
- FSH acts on granulosa cells
- increases activity of aromatase
- increases synthesis/secretion of 17β-estradiol
- increases activity of aromatase
- LH acts on theca cells
- 17β-estradiol synthesis requires granulosa cells and theca cells
- two-cell, two-gonadotropin model
- Estrogens potency
- 17β-estradiol > estrone > estriol
- Estrogen receptor
- estrogen receptor (ER) functions as a homodimer and resides in cell cytoplasm
- estrogen-ER complex translocates to cell nucleus, interacts with steroid response elements on chromatin, and rapidly induces transcription of target genes
- Function of estrogens
- at puberty, functions in development of female sex characteristics
- genitalia, breasts, and female fat distribution
- functions in proliferation and development of ovarian granulosa cells of follicles
- functions in maturation and maintenance of uterus
- proliferates endometrium of uterus
- lowers uterine threshold to contractile stimuli
- increases myometrial excitability
- upregulates estrogen, progesterone, and LH receptors
- positively feeds back on anterior pituitary at midcycle in response to LH surge
- ↑ FSH and ↑ LH
- stimulates prolactin secretion
- blocks action of prolactin on breasts
- upregulates transport proteins
- in blood plasma, estrogens are mostly bound to carrier proteins
- e.g., albumin and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)
- in blood plasma, estrogens are mostly bound to carrier proteins
- upregulates HDL cholesterol and downregulates LDL cholesterol
- at puberty, functions in development of female sex characteristics
- Notes
- pregnancy
- 50-fold ↑ in 17β-estradiol and estrone
- 1,000-fold ↑ in estriol
- pregnancy
- increase in estriol levels is an indicator of well-being of fetus
Progesterone
- Sources of progesterone
- corpus luteum, placenta, adrenal cortex, and testes
- Function of progesterone
- stimulates endometrial glandular secretions
- stimulates development of spiral arteries
- maintains pregnancy
- raises uterine threshold to contractile stimuli during pregnancy
- decreases myometrial excitability
- relaxes uterine smooth muscle
- prevents contractions
- produces thick cervical mucus that inhibits sperm entry into uterus
- increases basal body temperature
- increases hypothalamic temperature set-point
- negatively feeds back on anterior pituitary in luteal phase of menstrual cycle
- ↓ FSH and ↓ LH
- downregulates estrogen receptors
- Notes
- increase in biosynthesis of progesterone is characteristic of mid cycle or ovulation
- “PROGESTerone is PRO-GESTation”
Estrogen and Progesterone in Pregnancy
- Overview
- estriol is major estrogen in pregnancy
- Maternal-placental-fetal unit
- elevated levels of estrogens and progesterone are necessary for maintaining pregnancy
- corpus luteum is not adequate to generate very high hormone levels
- placenta emerges as major source of estrogens and progesterone
- placenta is an imperfect endocrine organ
- placenta cannot synthesize sufficient cholesterol
- cholesterol is a precursor for hormone synthesis
- placenta lacks necessary enzymes for estrogen synthesis
- placenta cannot synthesize sufficient cholesterol
- maternal-placental-fetal unit overcomes shortcomings of placenta to very high hormones levels
- Progesterone synthesis
- mother provides cholesterol (LDL particles) to placenta
- placenta converts cholesterol to pregnenolone then to progesterone
- placenta provides high progesterone levels to mother
- Estriol synthesis
- mother provides cholesterol (LDL particles) to placenta
- placenta converts cholesterol to pregnenolone to progesterone
- placenta provides high progesterone levels to fetus
- fetal adrenal cortex converts progesterone to DHEA-sulfate
- fetal liver hydroxylates DHEA-sulfate to 16-OH DHEA-sulfate
- fetus provides high levels of 16-OH DHEA-sulfate to placenta
- placenta converts 16-OH DHEA-sulfate to estriol
- placenta provides high estriol levels to mother



