Snapshot
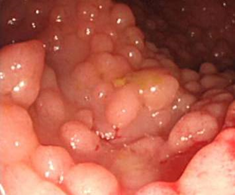
- A 17-year-old boy is seen after his annual colonoscopy. His mother and his older brother both died of colorectal cancer. Since 12 years old, he has been screened annually for colorectal cancer. This year, several hundred polyps are seen in his colon. Based on his own readings and his physician’s recommendation, he decides to undergo prophylactic colectomy.
Introduction
- Thousands of polyps in the intestinal tract from genetic mutation
- Genetics
- inactivating mutation in APC gene (adenomatous polyposis coli) on chromosome 5
- tumor suppressor gene
- 2-hit hypothesis
- remember, loss of APC is the beginning of the path to colorectal cancer
- inactivating mutation in APC gene (adenomatous polyposis coli) on chromosome 5
- Associated conditions
- Gardner syndrome
- AD subtype with colonic polyposis and bony and soft tissue tumors
- Turcot syndrome
- variants include autosomal recessive (AR) or AD with colonic polyposis and medulloblastoma or glioblastoma multiforme
- ↑ risk for colorectal cancer
- start screening with sigmoidoscopy at age 12 annually
- ↑ risk for other cancers
- hepatoblastoma
- thyroid cancer
- Gardner syndrome
- pancreatic cancer
Presentation
- Symptoms
- thousands of polyps develop at a young age
- rectum is always involved
- rectal bleeding or bloody stool
- abdominal discomfort
- thousands of polyps develop at a young age
- Physical exam
- rectal polyps may be palpable on rectal exam
- predicts FAP with 42% sensitivity and 97% specificity
Evaluation
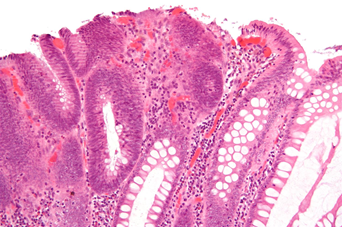
- Based on endoscopy, family history, and genetic testing
- Complete blood count with iron deficiency anemia
- Endoscopy with biopsy
- > 100 colorectal adenomatous polyps
- Genetic testing
- APC mutation
Differential
Treatment
- Prophylactic surgical colectomy
- Routine screening with colonoscopy and endoscopy
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- almost normal prognosis with colonic screening and colectomy
- Complications
- inevitable progression to colorectal cancer if no surgery
- at risk for other malignancies
- duodenal cancer
- hepatoblastoma
- thyroid cancer
- pancreatic cancer


