Snapshot
- A 10-year-old girl with a past medical history of epilepsy presents to the emergency room after sustaining a fall on the playground. She was fatigued and confused after the event and complained of pain in her wrist. On review of systems, she endorsed polyuria and polydipsia. Relevant medications included valproic acid, started 6 months ago, for her epilepsy. On physical exam, her right wrist was erythematous, swollen, and tender. Laboratory evaluation revealed hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and a mild metabolic acidosis.
Introduction
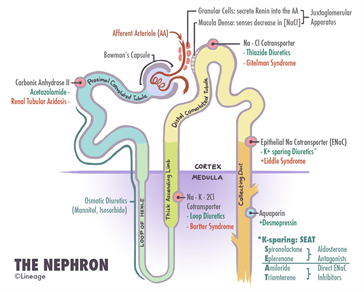
- Clinical definition
- a type of renal tubular acidosis (type 2) in the proximal convoluted tubules (PCT)
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- hereditary forms occur in 1:40,000
- demographics
- hereditary forms affect Caucasian children
- incidence
- Etiology
- hereditary conditions
- cystinosis
- most common genetic cause
- Wilson disease
- tyrosinemia
- galactosemia
- cystinosis
- multiple myeloma
- drugs
- cisplatin
- tenofovir
- valproic acid
- expired tetracyclines
- ifosfamide
- heavy metal poisonings
- hereditary conditions
- Pathogenesis
- defect in PCT causes problems in reabsorption of almost all amino acids, glucose, bicarbonate, phosphate, and potassium
- this causes all of the above to be excreted in the urine
- excretion of bicarbonate causes a metabolic acidosis
- defect is due to
- direct injury to PCT
- in genetic cases there is often a defective enzyme in nutrient metabolism that causes damage to the PCT
- light chains form crystals in PCT, causing damage
- defect in PCT causes problems in reabsorption of almost all amino acids, glucose, bicarbonate, phosphate, and potassium
- Associated conditions
- osteomalacia/rickets
- chronic ↓ phosphate and insufficient synthesis of vitamin D
- hypokalemia
- due to ↓ early Na+ reabsorption leading to ↑ K+ exchange
- osteomalacia/rickets
- Prognosis
- depends on etiology of Fanconi syndrome
- prognostic variable
- negative
- hereditary diseases
Presentation
- Symptoms
- primary symptoms
- renal disease
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- bone disease
- bone pain in the backs and hips
- pathologic fractures
- constitutional
- myalgias
- weight loss
- fatigue
- hereditary abnormalities
- failure to thrive
- developmental delay
- renal disease
- primary symptoms
- Physical exam
- signs of rickets
- bowed legs
- scoliosis
- signs of rickets
- teeth abnormalities
Studies
- Labs
- ↑ serum creatinine
- metabolic acidosis
- Urine studies
- aminoaciduria
- glycosuria
- phosphaturia
- urine pH < 5.5
- defect in bicarbonate reabsorption leads to increased excretion of bicarbonate in urine
- urine is then acidified by the intercalated cells in collecting tubule
- Diagnostic criteria
- no specific criteria, but these findings could suggest Fanconi syndrome
- increased excretion of amino acids, phosphates, and bicarbonate in the urine
- no specific criteria, but these findings could suggest Fanconi syndrome
- metabolic acidosis
Differential
- Distal renal tubular acidosis (type 1)
- urine pH > 5.5
- Hyperkalemic renal tubular acidosis (type 4)
- hyperkalemia and urine pH < 5.5
Treatment
- Conservative
- supportive care with fluid and electrolyte repletion
- indications
- if any metabolic derangements are found
- especially if hypokalemia or hypophosphatemia are found
- indications
- supportive care with fluid and electrolyte repletion
- Medical
- vitamin D (active form, cholecalciferol. or ergocalciferol)
- indications
- if osteomalacia is present
- indications
- bicarbonate
- indications
- vitamin D (active form, cholecalciferol. or ergocalciferol)
- metabolic acidosis
Complications
- Bone disease (osteomalacia, osteopenia, and osteoporosis)
- Renal insufficiency


