Overview
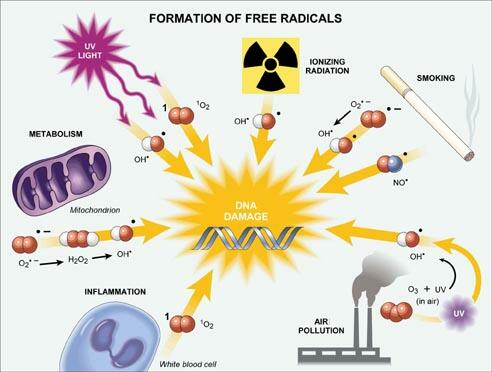
- Free radicals are chemical compounds with unpaired electrons in the valence shell
- a cascade is initiated whereby a free radical steals an electron from a cellular molecule
- the intial free radical is quenched but has created another free radical
- results in cell membrane peroxidation, DNA and protein damage
- Causes of free radical generation
- radiation exposure
- metabolism of drugs (phase I)
- e.g.) acetaminophen
- redox reactions
- naturally as part of oxidative ATP generation
- nitric oxide
- transition metals
- e.g.) copper and iron
- leukocyte oxidative burst
- Degradation of free radicals occus by
- enzymes
- catalase
- superoxide dismutase
- glutathione peroxidase
- spontaneous decay
- antioxidants
- vitamins A, C, E
- enzymes



