Snapshot
- An 8-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician for evaluation of increased urinary frequency. She has muscle cramps and fatigue. She is found to be normotensive. Laboratory exam reveals hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, and a mild metabolic alkalosis.
Introduction
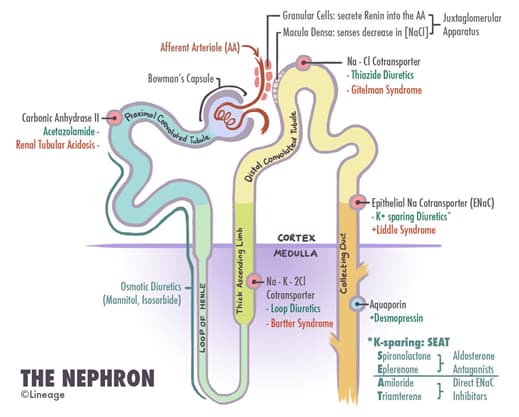
- Clinical definition
- a renal tubular defect affecting the distal convoluted tubules characterized by
- mild hypokalemia
- mild metabolic alkalosis
- significant hypomagnesemia
- normal blood pressure
- a renal tubular defect affecting the distal convoluted tubules characterized by
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- rare
- 1:40,000
- demographics
- detected in young children but can be detected in adulthood
- risk factors
- consanguinity
- incidence
- Pathogenesis
- mutation involving NaCl cotransporter (NCTT) which results in
- impaired Na+ reabsorption in distal convoluted tubule
- mutation involving NaCl cotransporter (NCTT) which results in
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal recessive
- mutations
- chromosome
- inheritance pattern
- SLC12A3 gene
Presentation
- Symptoms
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- muscle weakness or cramp
- fatigue
- paresthesias
- abdominal pain
- vomiting
- Physical exam
- growth is often normal but can be delayed
Studies
- Labs
- hypokalemia (lower than in Bartter’s)
- hypomagnesemia
- metabolic alkalosis
- genetic testing
- most definitive diagnosis
- Urine studies
- ↓ Ca2+
Differential
- Bartter’s syndrome
- normal serum magnesium
Treatment
- Conservative
- optimize electrolytes with diet or supplements
- indications
- those with hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia
- indications
- optimize electrolytes with diet or supplements
- Medical
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- indications
- for patients who require medical therapy beyond dietary supplements
- drugs
- indomethacin
- celecoxib
- indications
- potassium-sparing diuretics
- indications
- to treat hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis
- drugs
- amiloride
- indications
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- eplerenone
Complications
- Cardiac arrhythmia due to hypomagnesemia and hypokalemia
- Chondrocalcinosis


