Overview
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
- GFR is an important clinical tool used to assess patients with kidney disease
- this is an index of functional renal mass
- therefore, this data point can be used to determine the severity and course of renal disease
- this is an index of functional renal mass
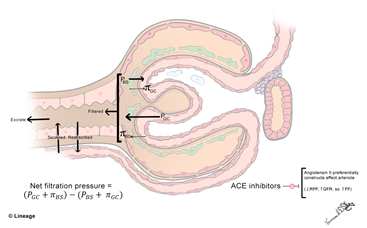
- Fluid movement across the glomerulus follows Starling’s law
- GFR = Kf [(PGC – PBS) – (πGC – πBS)]
- Kf is filtration coefficient
- water permeability or hydraulic conductance of glomerular capillary wall
- PGC is hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries
- PGC favors filtration
- acutely decreased after myocardial infarction
- PBS is hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s space
- PBS opposes filtration
- πGC is oncotic pressure in glomerular capillaries
- πGC opposes filtration
- chronically decreased by hypoalbuminemia
- πBS is oncotic pressure in Bowman’s space
- typically, πBS = 0
- Kf is filtration coefficient
- GFR = Kf [(PGC – PBS) – (πGC – πBS)]
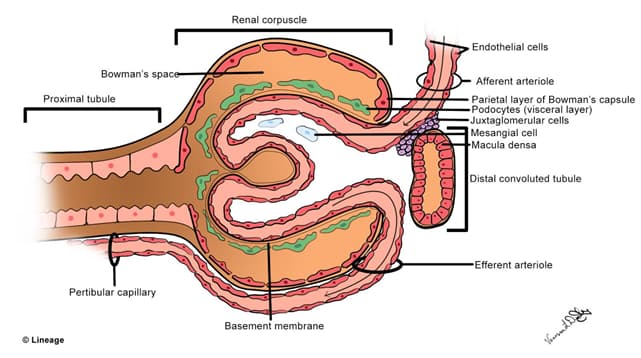
- Glomerular filtration rate and arteriolar resistance
- the glomerular capillaries are between the afferent (precapillary) and efferent (postcapillary) arteriole
- e.g., a drop in renal perfusion pressure (e.g., hypotension) stimulates the activation of the renin-angiotensin system which produces angiotensin II
- angiotensin II preferentially causes vessel constriction of the efferent arteriole
- this in turn increases PGC
- the idea is to prevent PGC from declining in the setting of hypotension
- this in turn increases PGC
- angiotensin II preferentially causes vessel constriction of the efferent arteriole
- e.g., a drop in renal perfusion pressure (e.g., hypotension) stimulates the activation of the renin-angiotensin system which produces angiotensin II
- the glomerular capillaries are between the afferent (precapillary) and efferent (postcapillary) arteriole
Measurement of Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
- GFR measurement (inulin)
- C(inulin) = GFR
- inulin is freely filtered across glomerular capillaries and is neither reabsorbed nor secreted
- inulin is a glomerular marker
- C(inulin) = [U(inulin) x V] / P(inulin) = GFR
- C(inulin) is clearance of inulin (mL/min)
- U(inulin) is urine concentration of inulin (mg/mL)
- V is urine flow rate (mL/min)
- P(inulin) is plasma concentration of inulin (mg/mL)
- normally, GFR ≈ 100 mL/min
- C(inulin) = GFR
- GFR measurement (creatinine)
- C(creatinine) ≈ GFR
- creatinine is freely filtered across glomerular capillaries and is moderately secreted by peritubular capillaries into tubular lumen
- C(creatinine) slightly overestimates GFR by 10-20%
- creatinine is freely filtered across glomerular capillaries and is moderately secreted by peritubular capillaries into tubular lumen
- C(creatinine) ≈ GFR


