Snapshot
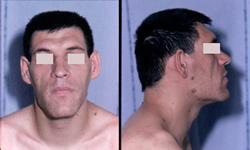
- A 52 year-old man complains of increased hat size and headaches when he wakes up in the morning. Physical exam reveals mild diastolic hypertension, prominant jaw with spaces between the teeth, large hands and feet, and generalized muscle weakness.
Introduction
- Benign pituitary adenoma that releases excess growth hormone
- Gigantism if the condition occurs before the fusion of the epiphysis
- Acromegaly if it occurs after skeletal epiphyseal closure
Presentation
- Symptoms
- Physical exam
- HTN
- due to the antinatriuretic action of GH
Evaluation
- Photographic changes
- for acromegalic features examine an old photograph to reveal changes in facial bones
- Serology
- hyperglycemia
- due to gluconeogenic action of GH
- hyperglycemia
- Suppression tests
- GH release not suppressed by glucose challenge
- MRI/CT
- shows enlargement of sella turcica on imaging
- Cardiomegaly on CXR
- hypertrophy of left ventricle
Treatment
- Surgical
- transphenoidal surgery
- Medical
- octreotide (somatostatin analogue)
- supresses GH release
- dopamine analog
- second line for refractory tumors
- GH receptor antagonists
- octreotide (somatostatin analogue)
- pegvisomant
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Cardiomegaly progressing to CHF is the most common cause of death


