Introduction
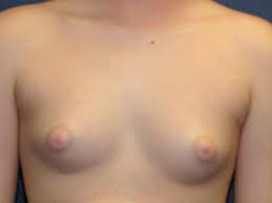
- Benign breast enlargement in males secondary to increased effective estrogen
- can be increased production or decreased degradation
- also result of decrease in androgens leaving estrogens unopposed
- May occur naturally throughout male life
- newborn
- secondary to high maternal estrogen
- elderly
- secondary to androgen decrease
- newborn
- Associated conditions
- cirrhosis
- genetic diseases
- Klinefelter syndrome
- increased aromatizing activity of Leydig cells
- high estrogen results in increased male breast cancer risk
- testicular feminization
- Klinefelter syndrome
- cancer
- choriocarcinoma of testis
- high production of hCG (an LH analogue)
- choriocarcinoma of testis
- drugs
- estrogen
- marijuana
- flutamide
- blocks androgen receptors
- leuprolide
- blocks androgen production
- psychoactive drugs
- “Some Drugs Create Awesome Knockers”
- Spironolactone
- block androgen receptors, displaces estrogen from SHBG
- Digitalis
- intrinsic estrogen activity
- Cimetidine
- Alcohol
- Ketoconazole
- displaces estrogen from SHBG
- Spironolactone


