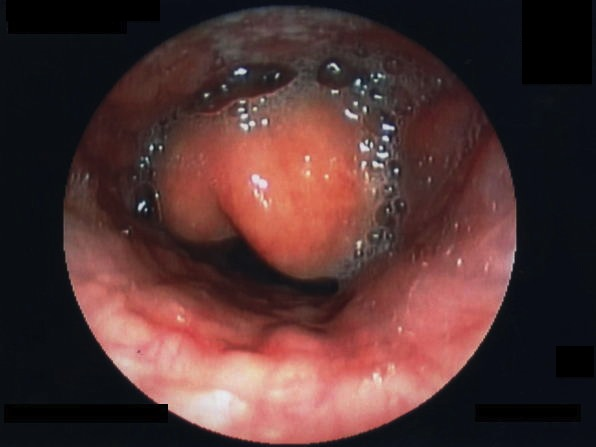
- A 6-year-old boy is brought to the pediatric emergency department after developing difficulty with breathing. Per his mother, his symptoms began approximately 3 hours ago and have progressively worsened. She endorses that he had an upper respiratory infection 1 week prior. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 100/65 mmHg, pulse is 105/min, and respirations are 28/min. Physical examination is notable for him appearing distressed with inspiration and leaning forward with his neck hyperextended and chin thrust forward. Laryngoscopy demonstrated an erythematous and edematous epiglottis. (Epiglottitis)
Introduction
- Classification
- gram-negative rod
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- nontypeable bacteria most commonly cause otitis media
- incidence
- Transmission
- respiratory
- Microbiology
- oxidase positive
- facultatively anaerobic
- nonmotile
- polysaccharide capsule
- there are 6 types of capsules; however, type b is commonly associated with invasive disease
- organisms without a capsule are said to be nontypeable
- IgA protease
- Associated conditions
- encapsulated (type b) strains
- meningitis
- epiglottitis
- septic arthritis
- nonencapsulated strains
- otitis media
- pulmonary disease in patients with preexisting lung disease (e.g., chronic bronchitis and viral influenza infection)
- encapsulated (type b) strains
- Prognosis
- haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine
- provides active immunization, which is important in preventing Hib infection
Studies
Presentation


