Introduction
- A condition characterized by the autoimmune destruction of the thyroid
- Pathophysiology
- the inflammatory reaction is a combination type II and type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- type II hypersensitivity reaction
- anti-TSH receptor antibodies are formed that inhibit thyroid hormone release
- opposite of Grave’s disease
- anti-TSH receptor antibodies are formed that inhibit thyroid hormone release
- type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- CD8 cells directly destroy thyroid tissue
- CD4-attracted macrophages destroy thyroid tissue
- type II hypersensitivity reaction
- the inflammatory reaction is a combination type II and type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- Genetics
- association with HLA-DR3, DR5 genotype
- Associated conditions
- chromosomal aneuploidies
Presentation
- Symptoms
- hyperthyroidism
- seen early in the disease course
- consequence of thryoid tissue destruction which releases stored thyroid hormones
- hypothyroidism
- seen later in the disease course
- after pre-formed thyroid hormone stores are released there is a decreased release as a result of impaired production
- hyperthyroidism
- Physical exam
- moderately enlarged, non-tender gland
Evaluation
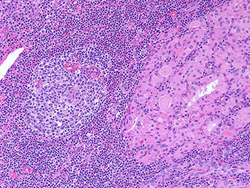
- Histology
- lymphocytic infiltrate
- germinal follicles
- Hürthle cells (eosinophilic-staining cells)
- fibrosis
Treatment
- Pharmacologic
- thyroid hormone supplementation
Complications
- Primary B-cell lymphoma of thyroid
- increased risk of primary B-cell lymphoma of thyroid


