Snapshot
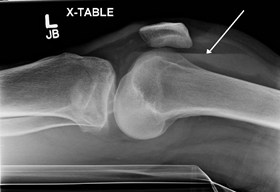
- A 4-year-old boy is brought into the emergency room after he is pushed on the playground. After falling to his knees, he develops grossly swollen and painful joints bilaterally, where the trauma occurred. Aspiration of the knee reveals frank blood. Platelet count and PT are normal. However, PTT is increased.
Introduction
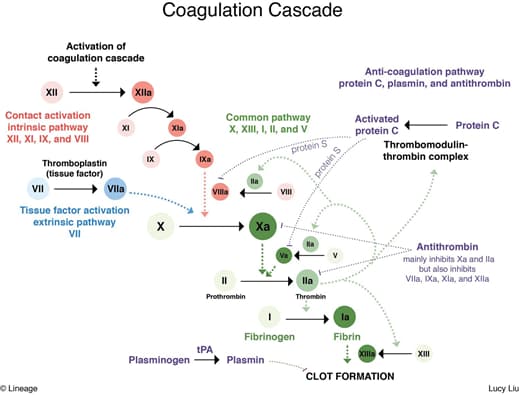
- Hereditary deficiencies in coagulation factors
- Intrinsic pathway coagulation defects
- hemophilia A
- deficiency of factor VIII
- hemophilia B
- deficiency of factor IX
- both lead to inadequate generation of thrombin
- hemophilia A
- Genetics
- both X-linked recessive
- Epidemiology
- almost exclusively in males
- Hemophilia A and B are clinically indistinguishable
Presentation
- Symptoms are similar in both hemophilia A and B
- spontaneous bleeding or bleeding following trauma or surgery
- hemoarthroses
- bleeding into joints
- easy bruising
- Physical exam
- swollen and painful joints
Evaluation
- ↑ PTT
- corrected with mixing studies
- indicates a factor deficiency
- corrected with mixing studies
- normal PT
- normal bleeding time
- most specific test
- functional assay for factor VIII or IX
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- Mild cases
- DDAVP for hemophilia A
- increases endogenous factor VIII
- DDAVP for hemophilia A
- Severe cases
- factor VIII or IX replacement
- Inhibitor cases
- immune tolerance induction
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- normal mortality
- Complications
- musculoskeletal complications
- synovitis
- arthropathy
- musculoskeletal complications


