Introduction
- Due to dual blood supply the liver does not typically infarct
- Flow can be obstructed in 3 places
- pre-hepatic
- intra-hepatic
- causes
- cirrhosis
- Budd-Chiari syndrome/centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis
- ischemic sequelae of heart failure
- centrilobular region perfused last and is the first to infarct
- causes
- post-hepatic
- caused by thrombosis of hepatic vein due to
- malignancy invasion (e.g. hepatocellular carcinoma)
- polycythemia vera
- hypercoagulable states (e.g. pregnancy)
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- occlusion of hepatic veins that causes blood to back up into the liver
- can lead to centrilobular congestion and necrosis
- congestive liver disease can ensue with symptoms of:
- hepatomegaly
- ascites
- varices
- abdominal pain
- liver failure
- potential causes
- polycythemia vera
- CHF
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- postpartum state
- hypercoaguable state
- anything that causes hepatic vein thrombosis
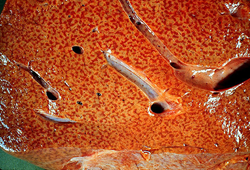
- pathological findings
- classicaly described as a “nutmeg liver”
- treatment
- sodium restriction
- anticoagulation:
- heparin
- warfarin
- surgical shunts
- liver transplanation in patient with fluminant liver failure
- congestive liver disease can ensue with symptoms of:
- can lead to centrilobular congestion and necrosis
- occlusion of hepatic veins that causes blood to back up into the liver
- caused by thrombosis of hepatic vein due to
- recurrence of disease is common
Presentation
- Physical exam
- pre-hepatic
- portal hypertension
- ascites
- NO hepatomegaly
- intra-hepatic
- hepatomegaly
- portal hypertension
- ascites
- post-hepatic
- hepatomegaly
- portal hypertension
- pre-hepatic
- ascites
Evaluation
- Intra-hepatic
- liver biopsy
- “nutmeg” appearance
- secondary to blood congestion/necrosis around central veins
- “nutmeg” appearance
- labs
- ↑ transaminases
- liver biopsy
- Post-hepatic
- ultrasound is test of choice
- labs
- ↑ transaminases


