Overview
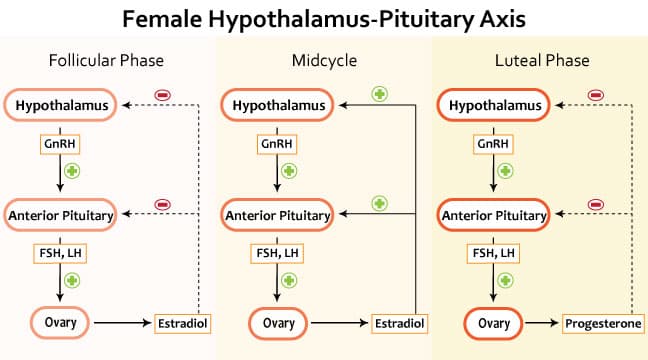
- Overview
- hypothalamic-pituitary axis controls 2 functions of ovaries
- oogenesis
- synthesis and secretion of female sex steroid hormones
- progesterone and 17β-estradiol (estrogen)
- hypothalamic-pituitary axis controls 2 functions of ovaries
- Hypothalamic-pituitary axis
- hypothalamus
- GnRH
- aka gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- pulsatile GnRH secretion via preoptic nucleus of hypothalamus
- GnRH travels in hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal blood system
- GnRH acts on gonadotrophs in anterior lobe of pituitary
- GnRH → ↑ FSH and ↑ LH (pulsatile)
- GnRH
- pituitary
- follicular phase of menstrual cycle
- LH
- aka luteinizing hormone
- FSH
- aka follicle-stimulating hormone
- FSH → (+) granulosa cells → ↑ 17β-estradiol
- FSH acts on granulosa cells
- increases activity of aromatase
- increases synthesis/secretion of 17β-estradiol
- androstenedione diffuses from theca cells to granulosa cells
- granulosa cells express 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- catalyzes conversion of androstenedione to testosterone
- granulosa cells express aromatase
- catalyzes conversion of testosterone to 17β-estradiol
- granulosa cells express 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- increases activity of aromatase
- FSH acts on granulosa cells
- negative feedback
- 17β-estradiol (via granulosa cells)
- ↑ 17β-estradiol → (-) hypothalamus → ↓ GnRH
- 17β-estradiol acts on hypothalamus
- downregulates GnRH secretion
- 17β-estradiol acts on hypothalamus
- ↑ 17β-estradiol → (-) anterior pituitary → ↓ FSH and ↓ LH
- 17β-estradiol acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- downregulates LH and FSH secretion
- 17β-estradiol acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- ↑ 17β-estradiol → (-) hypothalamus → ↓ GnRH
- 17β-estradiol (via granulosa cells)
- LH
- midpoint of menstrual cycle (ovulation)
- positive feedback
- 17β-estradiol (via granulosa cells)
- ↑↑ 17β-estradiol → (+) hypothalamus → ↑ GnRH
- 17β-estradiol acts on hypothalamus
- upregulates GnRH secretion
- 17β-estradiol acts on hypothalamus
- ↑↑ 17β-estradiol → (+) anterior pituitary → ↑↑ FSH, ↑↑ LH
- 17β-estradiol acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- upregulates LH, FSH secretion
- 17β-estradiol acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- ↑↑ 17β-estradiol → (+) hypothalamus → ↑ GnRH
- 17β-estradiol (via granulosa cells)
- positive feedback
- luteal phase of menstrual cycle
- LH surge
- ↑↑ LH → (+) corpus luteum → ↑ progesterone
- LH acts on corpus luteum
- increases synthesis/secretion of progesterone
- LH acts on corpus luteum
- ↑↑ LH → (+) corpus luteum → ↑ progesterone
- negative feedback
- progesterone (via granulosa lutein cells and theca lutein cells)
- ↑ progesterone → (-) hypothalamus → ↓ GnRH
- progesterone acts on hypothalamus
- downregulates GnRH secretion
- progesterone acts on hypothalamus
- ↑ progesterone → (-) anterior pituitary → ↓ FSH and ↓ LH
- progesterone acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- downregulates LH and FSH secretion
- progesterone acts on anterior lobe of pituitary
- ↑ progesterone → (-) hypothalamus → ↓ GnRH
- progesterone (via granulosa lutein cells and theca lutein cells)
- LH surge
- follicular phase of menstrual cycle
- hypothalamus


