Surfactant
- Alveolar Surface Tension
- surface tension generates a pressure that tends to collapse alveolus
- law of Laplace
- P = 2T/r
- P = collapsing pressure on alveolus = pressure required to keep alveolus open
- T = surface tension
- r = radius of alveolus
- pressure tending to collapse alveolus is directly proportional to surface tension generated by molecules of liquid lining alveolus (gas-liquid interface)
- pressure tending to collapse alveolus is indirectly proportional to alveolar radius
- large alveolus (large radius) has a low collapsing pressure
- small alveolus (small radius) has a high collapsing pressure
- surface tension → tendency for alveolar collapse on expiration
- expiration → ↓ alveolar radius
- P = 2T/r
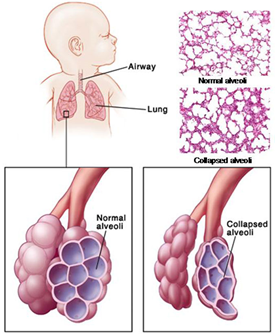
- Surfactant
- a mixture of phospholipids that line alveoli and reduce alveolar surface tension
- consists primarily of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC), or lecithin
- synthesized by type II pneumocytes
- ↓ alveolar surface tension → ↓ collapsing pressure on alveolus
- small alveolus remains open
- ↑ lung compliance → ↓ work of expanding lungs during inspiration
- without surfactant, small alveolus has a tendency to collapse (atelectasis)
- a mixture of phospholipids that line alveoli and reduce alveolar surface tension
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
- difficulty reinflating lungs
Additional Important Lung Products
- Prostaglandins
- Histamine
- binds receptors on smooth muscle cells
- induces vasodilation, bronchoconstriction
- binds receptors on smooth muscle cells
- Kallikrein
- catalyzes proteolytic cleavage of kininogens in kinin synthesis
- inactive kininogens → active kinins (e.g., bradykinin)
- e.g., bradykinin binds receptors on endothelial cells
- induces vasodilation, bronchoconstriction
- catalyzes proteolytic cleavage of kininogens in kinin synthesis
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)
- catalyzes angiotensin I → angiotensin II
- angiotensin II induces vasoconstriction
- acts as a kininase in kinin degradation
- ACE inactivates bradykinin
- ACE inhibitors → ↑ bradykinin → cough, angioedema
- catalyzes angiotensin I → angiotensin II


